What is the acceptable SEER rating?
The SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating is an important factor to consider when buying an AC system. It measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner and helps determine how much energy it consumes.
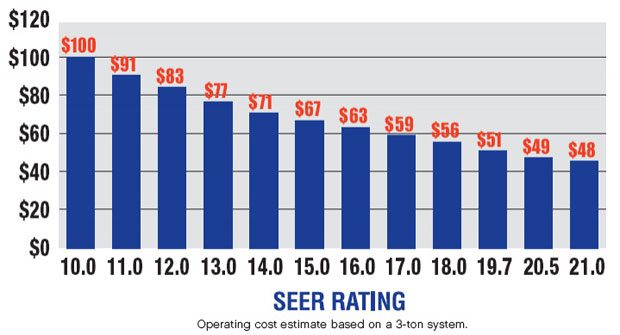
So, what is considered an acceptable SEER rating? In the United States, the minimum acceptable SEER rating for new AC systems is 14. However, the most efficient SEER rating available in the market is significantly higher.
If you want to ensure maximum energy efficiency and cost savings, it is recommended to choose an AC system with a SEER rating of at least 16 or higher.
The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the AC system will be. This means that you will not only save on your monthly energy bills but also reduce your carbon footprint. Investing in a high SEER rated AC system can also increase the resale value of your home, as energy efficiency is a key selling point in today’s market.
Understanding SEER Ratings for AC Systems
The SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating is a measure of the efficiency of an air conditioning system. It represents the ratio of the cooling output of an air conditioner to the electrical energy input. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the AC system is.
In the United States, the acceptable SEER rating for new residential air conditioning systems is determined by federal regulations. As of January 1, 2015, the minimum SEER rating for split system air conditioners is 14, while the minimum SEER rating for single-package air conditioners is 14 as well.
However, it is important to note that higher SEER ratings are available and can provide increased energy savings. AC systems with SEER ratings between 16 and 26 are considered high-efficiency units and can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to lower-rated systems.
It is also worth mentioning that the initial cost of a high SEER rated AC system may be higher than that of a lower-rated system. However, the energy savings over time can offset the higher upfront cost and result in long-term cost savings.
When choosing an air conditioning system, it is important to consider your specific cooling needs, climate conditions, and budget. Consulting with a reputable HVAC professional can help you determine the most suitable SEER rating for your AC system.
| 14 | Standard Efficiency |
| 16-26 | High Efficiency |
What is a SEER rating and why is it important?
The SEER rating, which stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measurement used to determine the efficiency of an air conditioning system. Specifically, it measures the cooling output of an AC unit during a typical cooling season, divided by the energy it consumes in watt-hours. In simple terms, the higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the air conditioner is.
SEER ratings can range from as low as 13 to as high as 26. The acceptable SEER rating may vary depending on factors such as climate, energy costs, and personal preferences. However, the minimum rating required by the U.S. Department of Energy for new residential central air conditioners is 14. This means that any new AC system installed in the United States must have a minimum SEER rating of 14.
So, why is the SEER rating important? Well, choosing an air conditioner with a high SEER rating can result in significant energy savings and lower utility bills. More efficient systems use less energy to cool your home, which not only helps the environment but also reduces your carbon footprint. Additionally, a higher SEER rating can also improve indoor comfort by providing better temperature and humidity control.
When shopping for a new AC system, it’s important to consider the SEER rating and choose a unit that suits your needs and budget. While a higher SEER rating often comes with a higher upfront cost, the long-term savings on energy bills can make it a worthwhile investment. It’s also worth noting that some utility companies offer rebates or incentives for purchasing high-efficiency air conditioners with a certain SEER rating, further reducing the cost of the system.
In summary, the SEER rating is an important factor to consider when selecting an air conditioning system. It measures the efficiency of the unit and can help you save money on energy bills while reducing your environmental impact. By understanding the acceptable SEER rating and its significance, you can make an informed decision and choose the most efficient AC system for your needs.
Factors that determine the SEER rating
The SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating for an air conditioning system is determined by several factors:
- The type and efficiency of the compressor: The compressor is the main component of an AC system. The type and efficiency of the compressor can significantly affect the SEER rating. High-efficiency compressors are designed to consume less electricity and provide better cooling performance.
- The size and layout of the unit: The size and layout of the AC unit can affect its efficiency. Units that are too small will have to work harder to cool a space, while units that are too large may cycle on and off frequently, leading to energy wastage.
- The quality of insulation: Proper insulation helps to prevent energy loss and improve the overall efficiency of the AC system. Well-insulated spaces require less cooling and therefore result in a higher SEER rating.
- The design of the air ducts: The design and condition of the air ducts can impact the efficiency of the AC system. Leaky or poorly insulated ducts can result in energy loss and reduced cooling performance.
- The location and climate: The location and climate of an area play a role in determining the SEER rating. Regions with hotter climates require AC systems with higher SEER ratings to provide efficient cooling.
- The efficiency of the refrigerant: The type and efficiency of the refrigerant used in the AC system can also affect the SEER rating. More environmentally friendly and energy-efficient refrigerants can result in higher SEER ratings.
It is important to consider these factors when choosing an AC system to ensure that you get the most efficient SEER rating for your specific needs and location.
SEER rating requirements by region
The SEER rating, also known as the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measure of the efficiency of an air conditioning system. It is a rating that determines how effectively an AC system can convert input energy into cooling output. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the system.
In the United States, SEER rating requirements vary by region. Each region has its own set of regulations and standards for minimum SEER ratings. These requirements are based on the climate conditions of the region, as well as environmental considerations.
In general, the minimum SEER rating for residential air conditioners in the United States is 13. However, some regions have higher requirements. For example, in the Southwestern region, which experiences hot and dry climates, the minimum SEER rating is typically 14 or 15. This is because more energy-efficient AC systems are needed to cope with the high cooling demands in these areas.
On the other hand, regions with milder climates may have lower SEER rating requirements. For instance, in the Northern region, where summers are shorter and less intense, the minimum SEER rating may be 13.
It is important to note that these are just guidelines, and there may be exceptions or variations within each region. It is always recommended to consult with local authorities, HVAC professionals, or refer to local building codes to determine the specific SEER rating requirements for your area.
How to choose the right SEER rating for your AC system?
When it comes to choosing the right SEER rating for your AC system, several factors need to be considered. The SEER rating, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, measures the cooling output of an air conditioning unit divided by the amount of energy it consumes. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the system is.
Firstly, it is important to check the acceptable SEER rating in your area. Different regions may have different regulations regarding the minimum SEER rating allowed for AC systems. This information can usually be found in local building codes or obtained from HVAC professionals.
Next, consider your financial situation and energy usage requirements. While higher SEER ratings offer greater energy efficiency and long-term cost savings, they often come with a higher upfront cost. It is essential to find a balance between energy efficiency and budget considerations that align with your specific needs and goals.
Additionally, consider the climate in which you live. If you reside in a hot and humid climate, a higher SEER rating may be more suitable to ensure the system operates efficiently and provides adequate cooling. On the other hand, if you live in a milder climate, a lower SEER rating may be sufficient to meet your cooling needs.
Consulting with an HVAC professional is highly recommended when choosing the right SEER rating for your AC system. They can assess your home’s specific cooling requirements, evaluate energy efficiency options, and provide expert guidance to help you make an informed decision.
Overall, choosing the right SEER rating for your AC system involves considering acceptable ratings, financial factors, climate conditions, and seeking professional advice. By taking the time to understand your options and make an informed decision, you can select an AC system with the optimal SEER rating to keep you comfortable while maximizing energy efficiency.
The benefits of a higher SEER rating
When it comes to choosing an air conditioning system, the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating is an important factor to consider. The SEER rating measures the energy efficiency of the system, with higher ratings indicating greater efficiency. But what are the benefits of a higher SEER rating?
1. Energy savings: A higher SEER rating means that your AC system is more efficient and consumes less energy. This can result in significant savings on your energy bills over time. In fact, according to the U.S. Department of Energy, upgrading from a SEER 9 to a SEER 13 system can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%.
2. Environmental impact: By using less energy, AC systems with higher SEER ratings help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a greener environment. Lower energy consumption also means a reduced demand on power plants, which can positively affect the overall energy grid.
3. Enhanced comfort: AC systems with higher SEER ratings are designed to provide more consistent cooling. They are able to maintain desired temperatures more efficiently, resulting in improved comfort levels inside your home. These systems also have better humidity control, helping to create a more comfortable indoor environment.
4. Long-term savings: While AC systems with higher SEER ratings may have a higher initial cost, the long-term savings in energy bills can offset the upfront investment. Additionally, many utility companies offer rebates or incentives for purchasing energy-efficient systems, further increasing the cost savings.
5. Durability and reliability: AC systems with higher SEER ratings often come with advanced features and components that are designed to enhance durability and reliability. This can result in less frequent repairs and a longer lifespan for the system, saving you money on maintenance and replacement costs.
In conclusion, opting for an AC system with a higher SEER rating has numerous benefits. From energy savings and environmental impact to enhanced comfort and long-term savings, choosing a more efficient system is a wise investment for both your wallet and the planet.
Cost considerations of higher SEER ratings
When it comes to choosing an air conditioning system, the SEER rating is an important factor to consider. The SEER rating, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, measures the efficiency of an AC unit. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the system is.
However, it’s essential to understand that higher SEER ratings often come with a higher price tag. While these energy-efficient systems can help you save on your energy bills in the long run, they may require a more significant upfront investment.
One of the main factors contributing to the increased cost of higher SEER ratings is the advanced technology used in these systems. Manufacturers incorporate innovative features and components to increase efficiency, such as variable speed compressors and improved insulation. These enhancements lead to higher production costs, which are reflected in the price of the unit.
Another cost consideration is the installation process. Higher SEER-rated systems often require specialized installation procedures or additional equipment, such as programmable thermostats or zoning systems. These extra requirements can increase the installation cost compared to a standard SEER-rated unit.
It’s important to weigh the initial investment against the potential long-term energy savings when considering a higher SEER rating. While a more energy-efficient system may cost more upfront, it can provide significant savings on your monthly utility bills over the lifespan of the system.
Moreover, many utility companies and government agencies offer rebates and incentives for purchasing higher SEER-rated systems. These incentives can help offset the initial cost and make a higher SEER rating more financially viable.
In conclusion, while a higher SEER rating is generally considered more efficient and environmentally friendly, it’s crucial to consider the associated costs. By evaluating the long-term energy savings potential, understanding the upfront investment, and researching available incentives, you can make an informed decision about the most suitable SEER rating for your air conditioning needs.
Common misconceptions about SEER ratings
There are several common misconceptions about SEER ratings that homeowners should be aware of when evaluating the energy efficiency of their air conditioning system.
| Misconception: | Explanation: |
| Higher SEER rating means better performance. | While a higher SEER rating generally indicates greater energy efficiency, it does not necessarily mean better performance. Other factors, such as proper installation and maintenance, also play a crucial role in the overall performance of an AC system. |
| The highest SEER rating available is always the best choice. | While it may seem logical to choose the AC system with the highest SEER rating available, it might not be the most cost-effective option for every homeowner. Factors such as climate, usage patterns, and budget should also be considered when selecting an appropriate SEER rating. |
| A higher SEER rating will instantly result in lower energy bills. | While a higher SEER rating can lead to energy savings, the actual impact on monthly energy bills will depend on various factors, such as the size of the living space, insulation, and the usage patterns of the occupants. |
| Increasing the SEER rating of an existing AC system will automatically improve energy efficiency. | Simply upgrading the SEER rating of an older AC system without considering factors such as ductwork, insulation, and proper sizing may not guarantee significant improvements in energy efficiency. |
By understanding these common misconceptions, homeowners can make more informed decisions when it comes to selecting the appropriate SEER rating for their AC system. It is important to consult with a qualified HVAC professional to ensure that the chosen SEER rating aligns with the specific needs and requirements of the home.
Energy savings with higher SEER ratings
The SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating is the measurement used to determine the energy efficiency of an air conditioning system. A higher SEER rating indicates a more efficient system that can provide greater energy savings.
When considering the SEER rating for your AC system, it is important to note that the acceptable SEER rating may vary depending on your location and climate. However, in general, a SEER rating of 14 or higher is considered to be acceptable and offers significant energy savings.
By upgrading to a higher SEER rated AC system, you can reduce your energy consumption and lower your utility bills. This is because a higher SEER rating means that the system uses less energy to cool your home, resulting in reduced energy costs.
In addition to energy savings, a higher SEER rating also provides environmental benefits. An energy-efficient AC system produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner and greener environment.
It is important to consult with a professional HVAC technician to determine the appropriate SEER rating for your specific needs and to ensure proper installation and maintenance.
In conclusion, investing in an air conditioning system with a higher SEER rating not only provides energy savings but also contributes to a more sustainable future.
SEER ratings and environmental impact
What is the acceptable SEER rating for your AC system? The SEER rating, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measure of the efficiency of an air conditioning unit. It represents the cooling output of the system divided by its electrical input and is used to determine how energy efficient the unit is.
But beyond just energy efficiency, SEER ratings also have an impact on the environment. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the system is, meaning it requires less energy to cool your home. This results in reduced energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing an air conditioning system with a higher SEER rating can have a significant positive impact on the environment. It not only helps reduce your carbon footprint but also helps conserve natural resources. By investing in a high SEER rating system, you can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
SEER rating regulations and certifications
The SEER rating, which stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measurement used to determine the energy efficiency of an air conditioning system. It represents the ratio of cooling output to the energy used, and a higher SEER rating indicates a more efficient system. But what is the acceptable SEER rating?
In the United States, the acceptable SEER rating is regulated by the Department of Energy (DOE). Their regulations specify the minimum SEER rating that new air conditioning systems must have in order to be sold and installed. Currently, the minimum SEER rating required for air conditioning systems varies based on the region of the country:
– In northern states, the minimum acceptable SEER rating is 13.
– In southern states, the minimum acceptable SEER rating is 14 or 14.5.
It’s important to note that these are just the minimum requirements set by the DOE, and many homeowners choose to purchase air conditioning systems with higher SEER ratings for increased energy savings and efficiency.
In addition to regulations, there are also certifications that air conditioning systems can obtain to demonstrate their energy efficiency. The most common certification for AC systems is the ENERGY STAR certification. In order to receive this certification, an air conditioning system must meet certain energy efficiency requirements, which include a minimum SEER rating. The specific requirements for ENERGY STAR certification can vary depending on the type and size of the AC system.
When choosing an air conditioning system, it’s important to consider both the SEER rating and any certifications it may have. By selecting a system with a higher SEER rating and reputable certifications, homeowners can ensure they are purchasing a system that will provide optimal energy efficiency and performance.
Maintenance tips for maintaining a high SEER rating
What is the acceptable SEER rating for your AC system? The SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating measures the efficiency of an air conditioning unit. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the system is in terms of energy consumption. Generally, the minimum acceptable SEER rating for a new AC system is 13, while the maximum can go up to 25.
To ensure that your AC system maintains a high SEER rating, here are some maintenance tips that you should follow:
1. Regularly clean and replace air filters: Dirty air filters can restrict airflow, making your AC work harder and consume more energy. Clean or replace your filters every 1-3 months, depending on the manufacturer’s recommendation.
2. Keep the condenser unit clean: The condenser unit, located outside, should be kept clear of debris such as leaves, grass, and dirt. Use a brush or vacuum to clean the fins and ensure proper airflow.
3. Schedule professional maintenance: Regular maintenance by a professional HVAC technician is essential for optimal performance. They can inspect and tune up your AC system, ensuring that it operates efficiently and identifying any potential issues.
4. Seal air leaks: Check for air leaks around windows, doors, and air ducts. Use weatherstripping and caulk to seal any leaks, preventing cool air from escaping and hot air from entering your home.
5. Utilize programmable thermostats: Programmable thermostats allow you to set energy-saving temperature schedules. Program your thermostat to adjust the temperature when you’re away or asleep to reduce energy consumption.
6. Maintain proper insulation: Insulate your home properly to prevent thermal energy loss. Ensure there is adequate insulation in your walls, attic, and basement to keep your home cool and reduce the workload on your AC system.
By following these maintenance tips, you can help maintain a high SEER rating for your AC system, ensuring energy efficiency, lower utility bills, and a comfortable indoor environment.
SEER rating comparisons for different AC systems
The SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating is a measure of how efficiently an air conditioning system operates. It is important to understand what the acceptable SEER rating is and what it means for the efficiency of your AC system.
SEER ratings can range from as low as 13 to as high as 25, with higher numbers indicating a more efficient system. In general, a SEER rating of 14 or higher is considered acceptable for residential air conditioning systems. However, some areas may have specific regulations or incentives that require a higher SEER rating.
When comparing AC systems based on their SEER ratings, it’s important to consider factors such as cost, energy savings, and environmental impact. Higher SEER-rated systems typically have a higher initial cost but can provide significant long-term energy savings. They also have a lower environmental impact, as they consume less energy and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
It’s also worth noting that the SEER rating is just one factor to consider when choosing an AC system. Other factors to consider include the size of the system, the ductwork in your home, and the climate in your area.
In conclusion, understanding the acceptable SEER rating is important when choosing an AC system. While a SEER rating of 14 or higher is generally considered acceptable, it’s important to consider factors such as cost, energy savings, and environmental impact when comparing different AC systems.
Q&A:
What is a SEER rating?
A SEER rating, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measure of the efficiency of an air conditioning system. It represents the cooling output divided by the electrical power input over a typical cooling season.
What is the acceptable SEER rating for AC systems?
The acceptable SEER rating for AC systems varies depending on the country and region. In the United States, the minimum SEER rating for new AC systems is 13, but higher ratings such as 16 or 18 are considered more efficient and can save more energy and money in the long run.
Is a higher SEER rating always better?
While a higher SEER rating generally indicates a more efficient AC system, the decision on what SEER rating is best depends on various factors such as climate, budget, and usage patterns. It is important to strike a balance between energy savings and upfront cost.
How can I determine the most efficient SEER rating for my AC system?
To determine the most efficient SEER rating for your AC system, you should consider factors such as your climate, energy costs, and long-term savings. Consult with an HVAC professional who can assess your specific needs and provide recommendations based on your situation.
What are the benefits of a higher SEER rating?
There are several benefits to having a higher SEER rating for your AC system. These include lower energy bills, reduced environmental impact, improved indoor comfort, and potentially higher home resale value. Additionally, some utility companies offer rebates or incentives for installing high-efficiency systems.