How much electricity does an AC use per hour?
An air conditioner (AC) is a common electrical appliance used to cool down indoor spaces. One important aspect to consider before investing in an AC is its energy consumption. Understanding how much electricity an AC uses per hour can help you estimate the cost and environmental impact of running your AC.
The amount of electricity consumed by an AC per hour depends on various factors, including its cooling capacity, efficiency rating, and usage patterns. ACs are typically rated in terms of British thermal units (BTUs) per hour, which indicates the amount of heat an AC can remove from a room in one hour.
The energy consumption of an AC is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) per hour. The energy efficiency of an AC is given by the seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) or the energy efficiency ratio (EER) rating. The higher the SEER or EER rating, the more energy-efficient the AC, meaning it consumes less electricity per hour to cool your space.
It’s essential to consider the energy consumption of an AC when comparing different models and deciding on the most suitable one for your needs. By choosing an energy-efficient AC and utilizing it wisely, you can not only save on your electricity bills but also reduce your carbon footprint.
Importance of understanding AC energy consumption
Understanding the energy consumption of an AC is crucial for several reasons:
- Cost: Knowing how much electricity an AC uses per hour can help you estimate the cost of running it. This information can assist you in budgeting and managing your electricity expenses.
- Eco-friendliness: By understanding the energy consumption of your AC, you can make informed choices that contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle. You can choose energy-efficient models or adjust the temperature settings to reduce your carbon footprint.
- Efficiency: Understanding the energy consumption of an AC allows you to assess its efficiency. By comparing the energy usage of different models, you can make a more informed decision when purchasing an AC and prioritize energy-saving features.
- Maintenance: Being aware of your AC’s energy consumption can help you identify any unusual spikes in electricity usage. This can indicate potential issues or the need for maintenance, helping you prevent costly repairs or breakdowns.
- Energy Conservation: Understanding AC energy consumption promotes energy conservation. By being conscious of the amount of electricity your AC uses, you can take steps to minimize usage, such as adjusting temperature settings, improving insulation, or using alternative cooling methods when appropriate.
In summary, understanding AC energy consumption not only allows you to manage costs and make eco-friendly choices but also helps in maintaining efficiency, identifying maintenance needs, and promoting energy conservation. It is an essential aspect of responsible AC usage.
Factors influencing AC energy consumption
When it comes to air conditioning, there are several factors that can influence energy consumption. Understanding these factors can help you estimate how much electricity an AC unit will use per hour.
One of the main factors is the size and capacity of the AC unit. Larger units will generally require more energy to operate compared to smaller units. The cooling capacity of the AC unit is measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units), and the higher the BTU rating, the more electricity it will use.
The temperature setting is another important factor. The lower you set the temperature, the more energy the AC unit will use. It’s recommended to set the thermostat to the highest comfortable temperature to reduce energy consumption.
The insulation of your home is also a significant factor. If your home is well-insulated, it will retain cool air more effectively, reducing the workload on the AC unit and ultimately lowering energy consumption.
The efficiency of the AC unit itself plays a crucial role. AC units with higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings are more energy-efficient and will use less electricity. It’s worth investing in a higher SEER-rated unit to save on energy costs in the long run.
The climate in which you live is another factor to consider. If you live in a hot and humid climate, your AC unit will need to work harder to cool your home, resulting in higher energy consumption.
Lastly, the frequency and duration of AC usage will impact energy consumption. If you use your AC unit for longer periods or frequently switch it on and off, it will use more electricity.
| Size and capacity of the AC unit | Higher BTU rating requires more electricity |
| Temperature setting | Lower temperature setting increases energy usage |
| Insulation of the home | Well-insulated homes conserve cool air, reducing AC workload |
| Efficiency of the AC unit | Higher SEER rating results in lower energy consumption |
| Climate | Hotter and more humid climates require more AC energy |
| Frequency and duration of AC usage | Longer or frequent usage leads to higher energy consumption |
Efficiency ratings and their impact on energy consumption
One important factor to consider when determining the energy consumption of an air conditioner is its efficiency rating. Efficiency ratings measure how effectively the AC unit converts electricity into cool air. The higher the efficiency rating, the less electricity an AC unit will consume per hour.
When an air conditioner has a high efficiency rating, it can provide the same level of cooling while using less electricity compared to a lower efficiency unit. This means that AC units with higher efficiency ratings can help reduce energy consumption and ultimately save you money on your electricity bill.
Efficiency ratings are typically expressed in terms of seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) or energy efficiency ratio (EER). SEER ratings measure the cooling output of an air conditioner during a typical cooling season divided by the total electric energy input during the same period. EER ratings, on the other hand, measure the cooling capacity of an AC unit divided by its total electrical power consumption at a specific outdoor and indoor temperature.
By choosing an air conditioner with a higher efficiency rating, you can significantly reduce your energy consumption. This not only benefits your wallet but also has a positive impact on the environment by decreasing the demand for electricity generated from fossil fuels.
AC energy consumption per hour: Explained
Have you ever wondered how much electricity an AC unit uses per hour? Understanding the energy consumption of air conditioners can help you make informed decisions about energy usage and costs.
The amount of electricity an AC uses per hour depends on several factors, including the size and efficiency of the unit, the temperature setting, and the climate conditions. Generally, the larger the AC unit and the lower the temperature setting, the more electricity it will consume.
On average, a typical residential central air conditioner in the United States uses about 3,500 to 5,000 watts of electricity per hour. This means that if you run your AC for 10 hours a day, it could use up to 50,000 watt-hours or 50 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity.
It is important to note that AC energy consumption can vary significantly depending on factors such as insulation levels, usage patterns, and thermostat settings. Additionally, newer energy-efficient AC units are designed to consume less electricity compared to older models.
To estimate how much electricity your AC unit uses per hour, you can refer to its energy efficiency rating, also known as the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio). The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the unit is, and the less electricity it will use.
Reducing the energy consumption of your AC unit can help lower your electricity bills and reduce your environmental impact. Some tips for improving energy efficiency include properly insulating your home, maintaining your AC unit regularly, and adjusting the temperature settings to more moderate levels.
By understanding how much electricity an AC unit uses per hour, you can make smarter choices about energy usage and potentially save money in the long run. Remember to consult your AC unit’s documentation or speak with a professional for more specific information about its energy consumption.
Different types of AC units and their energy usage
When it comes to air conditioning, there are various types of AC units available on the market. Each type has its own energy usage, which determines how much electricity the AC unit will consume per hour.
Window AC units are the most common type of air conditioners. These units can cool a single room and are typically installed in a window or a small opening in a wall. Window AC units generally range in size from 5000 to 25000 BTUs (British Thermal Units) and their energy usage can vary accordingly. On average, a window AC unit can consume around 500 to 1500 watts of electricity per hour.
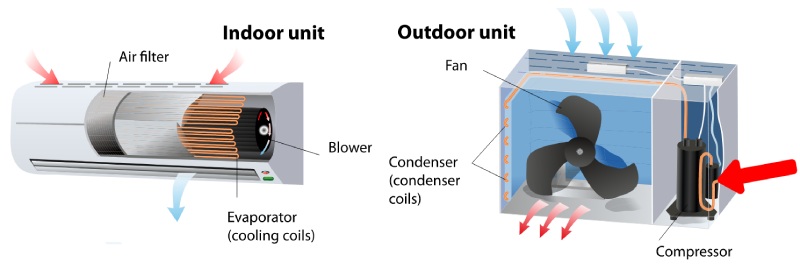
Another type of AC unit is the split system. Split systems consist of an indoor unit and an outdoor unit. The indoor unit is typically mounted on a wall or ceiling, while the outdoor unit is placed outside the building. Split systems are more efficient than window AC units and can cool multiple rooms. The energy usage of split systems varies depending on their size and capacity, but on average, they consume around 1000 to 2000 watts of electricity per hour.
Ducted AC units are designed to cool an entire house or building. They utilize a network of ducts to distribute cool air throughout the space. Ducted AC units are usually more energy-efficient compared to window and split systems, but their energy usage can be higher due to the larger area they cover. Depending on the size and capacity, ducted AC units can consume anywhere from 2000 to 5000 watts of electricity per hour.
Portable AC units are another popular option, especially for those who live in apartments or rented spaces. These units can be easily moved from one room to another and do not require any installation. Portable AC units typically have a lower cooling capacity compared to other types of AC units, so their energy usage tends to be lower as well. On average, portable AC units can consume around 500 to 1000 watts of electricity per hour.
It’s important to note that these are just average energy consumption values and the actual usage may vary depending on various factors such as the size of the room, insulation, temperature settings, and usage patterns.
How to calculate AC energy consumption
Calculating the energy consumption of an AC unit can help you understand how much electricity it uses per hour. By knowing this information, you can estimate the cost of running your AC and make informed decisions about energy usage.
Here are the steps to calculate AC energy consumption:
- Identify the AC unit’s power rating: Look for the unit’s power rating, typically measured in watts (W), on the manufacturer’s label or in the user manual.
- Convert the power rating to kilowatts (kW): Since most electric bills are calculated in kilowatt-hours (kWh), you need to convert the power rating from watts to kilowatts by dividing it by 1000 (1 kW = 1000 W).
- Calculate the energy consumption per hour: Multiply the AC unit’s power rating in kilowatts by the number of hours it runs per day. The result will be the amount of energy consumed by the AC unit in kilowatt-hours (kWh) per day.
For example, if an AC unit has a power rating of 1500 W and runs for 8 hours per day, the energy consumption per day would be:
1500 W ÷ 1000 = 1.5 kW
1.5 kW × 8 hours = 12 kWh per day
Keep in mind that this calculation only provides an estimate of energy consumption. Factors such as the AC unit’s energy efficiency, temperature settings, and usage patterns can influence the actual energy usage.
By understanding how to calculate AC energy consumption, you can monitor and manage your electricity usage efficiently, potentially reducing your energy costs and environmental impact.
Average AC energy consumption per hour in different countries
When it comes to cooling down our homes or offices, air conditioners are essential. However, many people are concerned about the electricity consumption of these appliances.
So, how much electricity does an AC use per hour? The answer varies depending on several factors, such as the type and size of the air conditioner, the temperature settings, and the efficiency of the unit. Additionally, the energy consumption can also vary from one country to another.
Research shows that the average AC energy consumption per hour in different countries can range from 0.5 kWh to 2 kWh. This means that the amount of electricity an AC uses per hour can vary significantly depending on where you are.
For example, in countries with hotter climates like Saudi Arabia or the United Arab Emirates, where air conditioners are used extensively throughout the year, the energy consumption can be higher due to the constant need for cooling. On the other hand, in countries with milder climates like Sweden or Canada, the energy consumption may be lower as air conditioners are not used as frequently.
It’s worth noting that these are just average values, and individual AC units can have different energy consumption rates. Additionally, energy-saving features, such as inverter technology, can also affect the energy consumption of an air conditioner.
To estimate the electricity consumption of your AC per hour, it’s best to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications or consult with a professional. By understanding the energy consumption of your air conditioner, you can make informed decisions about energy usage and potentially save on your electricity bills.
The impact of temperature settings on AC energy consumption
When it comes to the energy consumption of an air conditioner (AC), one of the key factors that greatly affects it is the temperature setting. The temperature setting determines how hard the AC needs to work in order to cool the room to the desired level.
Per hour, an AC unit uses electricity to run its compressor, fan, and other components. The more the AC needs to run, the more electricity it will consume. So, understanding the impact of temperature settings is essential for optimizing energy usage and reducing electricity bills.
Generally, the lower the temperature setting, the more energy the AC will consume. This is because the AC needs to work harder and for longer periods to maintain a lower temperature. For example, setting the AC to 65 degrees Fahrenheit will require more energy than setting it to 75 degrees Fahrenheit.
To demonstrate the impact of temperature settings on energy consumption, consider the following table:
| 65 degrees Fahrenheit | High |
| 70 degrees Fahrenheit | Moderate |
| 75 degrees Fahrenheit | Low |
As shown in the table, a temperature setting of 65 degrees Fahrenheit will result in higher AC energy consumption compared to a temperature setting of 75 degrees Fahrenheit. Therefore, it is recommended to set the AC to a reasonable and comfortable temperature that helps save energy without compromising on comfort.
In conclusion, the impact of temperature settings on AC energy consumption cannot be overstated. By understanding and optimizing the temperature settings, it is possible to significantly reduce energy usage and save on electricity bills while still enjoying a comfortable indoor environment.
How to reduce AC energy consumption
When it comes to cooling your space, air conditioners can consume a significant amount of electricity. However, there are several steps you can take to reduce the energy consumption of your AC unit. By following these tips, you can not only save money on your utility bills, but also contribute to a more sustainable environment.
| 1 | Set your thermostat to a higher temperature |
| 2 | Use a programmable thermostat |
| 3 | Keep doors and windows closed |
| 4 | Utilize ceiling fans |
| 5 | Seal and insulate your home |
| 6 | Keep air vents clear and unobstructed |
| 7 | Clean or replace air filters regularly |
| 8 | Use shades or blinds to block out sunlight |
| 9 | Avoid using heat-generating appliances during the hottest times of the day |
| 10 | Maintain regular AC maintenance |
By implementing these energy-saving measures, you can effectively reduce the amount of electricity your AC unit uses per hour, resulting in a more efficient and cost-effective cooling system.
Energy-saving alternatives to air conditioners
If you are concerned about the electricity usage and environmental impact of using an AC, there are several energy-saving alternatives available. These alternatives can help keep your space cool while reducing your carbon footprint.
Fans: Using fans to circulate air in your home or office can help create a cooling effect by evaporating moisture from your skin. Compared to air conditioners, fans consume much less electricity per hour and are a more energy-efficient option.
Natural ventilation: Opening windows and doors to let in fresh air can help to cool down your living or working space. Taking advantage of natural ventilation can be particularly effective during cooler times of the day, such as early morning or late evening.
Insulation: Properly insulating your home or office can help keep the indoor temperature stable and reduce the need for excessive cooling. Insulation helps to prevent heat transfer between the interior and exterior, reducing the workload on air conditioners or other cooling systems.
Shading: Installing blinds, curtains, or reflective films on windows can help block out direct sunlight and keep your space cooler. By reducing the amount of heat entering your space, you can decrease the demand for air conditioning and save on electricity usage.
Heat-reducing materials: Using materials with heat-reducing properties, such as light-colored roofing or reflective coatings on walls, can help to keep your space cooler. These materials reflect the rays of the sun, reducing the amount of heat absorbed by the building and reducing the need for air conditioning.
Ceiling fans: Installing ceiling fans in your home or office can help to circulate air and create a cooling effect. Ceiling fans use less electricity compared to air conditioners and can be an efficient way to maintain a comfortable temperature.
Energy-efficient HVAC systems: If you still require a cooling system, consider investing in an energy-efficient HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system. These systems can operate at higher efficiencies and consume less electricity compared to traditional air conditioners, helping to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
By exploring these energy-saving alternatives, you can minimize your electricity usage while still keeping your space cool and comfortable. These options not only reduce your energy bills but also contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle.
The role of AC maintenance in reducing energy consumption
How much electricity does an AC use per hour?
An air conditioner (AC) is a common appliance used to cool down a space and maintain a comfortable temperature. However, it consumes a significant amount of electricity in the process. Understanding the energy consumption of an AC can help individuals make informed decisions to reduce their energy usage.
An AC unit’s energy consumption is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) per hour.
On average, a central air conditioning system can use anywhere from 1.5 kWh to 3.5 kWh per hour, depending on factors such as the size of the unit, the local climate, and the desired indoor temperature.
The importance of AC maintenance in reducing energy consumption cannot be overstated.
Regular maintenance such as cleaning or replacing air filters, inspecting and cleaning the condenser and evaporator coils, and checking for refrigerant leaks can significantly improve an AC unit’s energy efficiency.
Dirty air filters can block airflow and force the unit to work harder, increasing its energy consumption.
Clogged condenser and evaporator coils reduce heat transfer and can lead to inefficient cooling, resulting in higher electricity usage.
Refrigerant leaks can cause the AC to overwork as it tries to maintain the desired temperature, leading to increased energy consumption.
By maintaining the AC unit properly, individuals can ensure that it functions at its optimal level, reducing energy consumption and ultimately saving on electricity costs.
Case study: Energy consumption of a typical residential AC
One of the main concerns for homeowners who have air conditioners (AC) is the amount of electricity these units consume. Understanding the energy consumption of an AC is essential for budgeting and reducing environmental impact.
To determine how much electricity a typical residential AC uses per hour, a case study can be conducted. In this study, a commonly available AC model will be analyzed to provide an estimate of its energy consumption.
Firstly, it is important to note that the energy consumption of an AC can vary depending on several factors such as its cooling capacity, efficiency rating, climate conditions, and usage patterns. However, we can use a typical value for the purpose of our case study.
On average, a typical residential AC unit with a cooling capacity of 12,000 BTU (British Thermal Units) consumes around 1,200 to 1,500 watts of electricity per hour during operation. It is important to note that this is just an estimate, and actual energy consumption can vary.
It’s worth mentioning that newer models of air conditioners are often more energy-efficient than older ones. Energy-efficient features such as variable speed fans, programmable thermostats, and high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings can significantly reduce energy consumption. Homeowners should consider these factors when purchasing an AC to minimize energy usage.
If you are concerned about the electricity consumption of your AC, there are a few steps you can take to lower it. Firstly, setting the thermostat to a higher temperature when you are not at home can help reduce the workload on the AC and save energy. Additionally, regular maintenance and cleaning of the AC unit, including replacing filters, can help optimize its performance and energy efficiency.
In conclusion, a typical residential AC can consume around 1,200 to 1,500 watts of electricity per hour during operation. By considering energy-efficient features and adopting smart usage habits, homeowners can effectively manage the energy consumption of their ACs while maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
The environmental impact of AC energy consumption
AC energy consumption is measured in terms of how much electricity an AC unit uses per hour. The environmental impact of this energy consumption can be significant. AC units require a large amount of electricity to function, especially when running for extended periods of time.
Electricity generation is one of the leading contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, which are a major driver of climate change. The more electricity that is used, the greater the demand on power plants to generate that electricity, and the more greenhouse gases are emitted as a result.
In addition to greenhouse gas emissions, the production and disposal of AC units also have environmental impacts. The manufacturing process requires the extraction of raw materials and the use of energy, both of which can contribute to pollution and resource depletion. At the end of their lifespan, AC units can also become e-waste, which presents its own set of challenges for proper disposal and recycling.
Considering the environmental impact of AC energy consumption is important in order to make more sustainable choices. This can include opting for energy-efficient AC units, using them sparingly, and exploring alternative cooling methods that are less energy-intensive. Additionally, investing in renewable energy sources can also help reduce the carbon footprint associated with AC energy consumption.
Government regulations and initiatives to reduce AC energy consumption
In an effort to promote energy efficiency and reduce electricity consumption, governments around the world have implemented various regulations and initiatives pertaining to air conditioners (ACs).
One common regulation is the requirement for AC manufacturers to adhere to minimum energy efficiency standards. These standards specify the maximum amount of electricity that an AC can use per hour of operation. By setting these limits, governments aim to encourage the production and use of energy-efficient AC units.
Additionally, some governments have introduced labeling programs that provide consumers with information about the energy efficiency of different AC models. These labels typically include an energy efficiency rating, allowing consumers to compare the electricity consumption of various AC units before making a purchase. This initiative helps raise awareness about energy-efficient options and encourages consumers to choose ACs with lower electricity usage.
Furthermore, governments also promote the adoption of energy-saving practices through educational campaigns and incentive programs. These initiatives aim to educate the public on the benefits of using ACs sparingly and efficiently. For instance, campaigns may emphasize the importance of setting the AC temperature at a moderate level, ensuring proper insulation of buildings, and regular maintenance of AC units. Incentives such as tax rebates or subsidies for purchasing energy-efficient ACs and using them responsibly can also incentivize consumers to reduce their electricity consumption.
Overall, government regulations and initiatives play a significant role in reducing AC energy consumption. By setting energy efficiency standards, providing information through labeling programs, and promoting energy-saving practices, governments aim to decrease the environmental impact and reliance on electricity for cooling purposes.
| United States | Energy Star program |
| European Union | Ecodesign Directive |
| Japan | Top Runner program |
Q&A:
How much electricity does an AC use per hour?
The amount of electricity an AC uses per hour varies depending on the size, efficiency, and usage of the AC unit. On average, a central air conditioner can use around 3,500 watts per hour, while a window unit can use between 500 and 1,500 watts per hour.
Is it expensive to run an AC all day?
Running an AC all day can result in higher electricity bills. The cost of running an AC depends on factors such as the size of the unit, electricity rates, and desired temperature. However, it is generally more cost-effective to use energy-saving settings, such as setting the thermostat at a moderate temperature and using energy-efficient models.
What factors affect the electricity consumption of an AC?
The electricity consumption of an AC can be affected by various factors, such as the size of the unit, the efficiency rating, the temperature setting, the duration of usage, and the insulation of the building. It is important to choose the right size and model of AC for your space and to properly maintain and insulate your home to reduce energy consumption.
How can I reduce the energy consumption of my AC?
There are several ways to reduce the energy consumption of your AC. You can start by setting the thermostat at a moderate temperature and using energy-saving settings, such as programmable thermostats. Proper insulation and sealing of windows and doors can also help to reduce energy loss. Regular maintenance and cleaning of the AC unit can improve its efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Are there any energy-efficient models of AC available?
Yes, there are energy-efficient models of AC available in the market. These models are designed to use less energy while providing the same level of cooling. Look for AC units with a high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating, as higher SEER ratings indicate better energy efficiency. Energy Star certified AC units are also a good choice as they meet strict energy efficiency guidelines.
How much electricity does an AC use per hour?
The amount of electricity an AC uses per hour depends on several factors, such as the size and efficiency of the AC unit, the temperature settings, and the insulation of the space being cooled. On average, a central AC unit can consume anywhere between 1,200 to 2,400 watts per hour.
What are the most energy-efficient AC units?
The most energy-efficient AC units are those with a high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating. A SEER rating measures the cooling output of an AC unit divided by the energy it consumes. AC units with a SEER rating of 14 or higher are considered energy-efficient. Additionally, inverter AC units are known for their energy-saving capabilities as they can adjust their cooling capacity based on the actual requirement.