Does an AC take a lot of electricity?
Air conditioners are a common appliance in households and commercial buildings, especially in hot climates. They provide much-needed relief from the scorching heat, but have you ever wondered how much electricity they actually consume? The answer might surprise you.
Firstly, it’s important to note that air conditioners do take up a lot of electricity. This is because they have to power various components, such as the compressor, fan, and condensing unit, to cool down the warm air and circulate it throughout the room. These components require a significant amount of energy to function effectively.
On average, a standard air conditioner can consume anywhere from 500 to 1500 watts of electricity per hour when in use. This can add up quickly, especially if the air conditioner is running for extended periods of time or if multiple units are being used simultaneously. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the energy efficiency of an air conditioner when purchasing one, as it can greatly impact your electricity bills.
It’s worth noting that newer models of air conditioners are designed to be more energy-efficient, with various features such as programmable thermostats and energy-saving modes. These advancements can help reduce the amount of electricity consumed by the air conditioner, ultimately saving you money in the long run. Additionally, proper maintenance and regular cleaning of the air conditioner can also contribute to its energy efficiency.
In conclusion, air conditioners do require a significant amount of electricity to operate effectively. However, with the advancement of technology and the availability of energy-efficient models, it is possible to enjoy the benefits of air conditioning while keeping your electricity consumption in check.
Understanding the Energy Consumption of Air Conditioners
Air conditioners (AC) are a common household appliance that many people rely on to keep their homes cool during hot summer months. However, not everyone understands the impact that these devices can have on their electricity bill.
It is important to take into account the energy consumption of an AC unit when considering its use. ACs can take up a significant amount of electricity, especially if they are running for long periods of time or if they are not properly maintained.
An AC unit usually consumes electricity in two ways. First, it requires electricity to power the fans that circulate the air and cool the room. Second, it requires electricity to power the compressor, which is responsible for cooling the air. The amount of electricity that an AC unit consumes will depend on factors such as the size of the unit, its efficiency rating, and how often it is used.
It is important to note that not all AC units are created equal in terms of energy consumption. Some models are designed to be more energy-efficient than others, meaning they use less electricity to achieve the same level of cooling. When purchasing an AC unit, it is important to look for the Energy Star label, which indicates that the unit meets certain energy efficiency standards.
To reduce the energy consumption of your AC unit, there are several steps you can take. First, you can set the thermostat to a higher temperature when you are not at home or are sleeping, as this will reduce the amount of time the AC unit is running. Additionally, you can ensure that your home is properly insulated and that windows and doors are sealed, as this will help prevent cool air from escaping.
In conclusion, understanding the energy consumption of an AC unit is important for both environmental and financial reasons. By considering factors such as the efficiency rating of the unit and taking steps to reduce energy consumption, you can help lower your electricity bill and minimize your impact on the environment.
Why is it important to know?
Understanding the energy consumption of an air conditioner is crucial for several reasons:
- Awareness: Knowing how much electricity an AC unit uses can help individuals and businesses be aware of their energy usage and make informed decisions about their cooling needs.
- Cost savings: Air conditioners can be a major consumer of electricity, especially during hot summer months. Knowing the energy consumption of an AC unit can help users estimate their electricity bills and implement energy-saving practices to reduce costs.
- Environmental impact: Air conditioners contribute to greenhouse gas emissions which can have a significant impact on global climate change. By understanding the energy consumption of AC units, individuals and businesses can take steps to minimize their carbon footprint and reduce environmental harm.
- Efficiency: Being aware of the energy consumption of different AC units can help users choose more energy-efficient models. Energy-efficient air conditioners can provide the same level of cooling while using less electricity, helping users save money and reduce their environmental impact.
- Planning: For businesses or organizations that rely heavily on air conditioning, knowing the energy consumption of AC units is essential for planning purposes. It helps in budgeting for electricity costs and determining the capacity and number of AC units required for efficient cooling.
Overall, understanding the energy consumption of air conditioners enables individuals, businesses, and communities to make sustainable choices, reduce costs, and minimize their impact on the environment.
Factors that affect energy consumption
When it comes to the energy consumption of air conditioners, there are a lot of factors that can influence how much electricity they use. These factors can include:
- The temperature you set the AC to: The lower you set the temperature, the more energy the air conditioner will need to reach and maintain that cool temperature.
- The size of the AC unit: Larger AC units tend to consume more electricity compared to smaller ones, as they have a greater cooling capacity.
- The efficiency of the AC unit: AC units with higher energy efficiency ratings consume less electricity to produce the same amount of cooling compared to less efficient units.
- The insulation of your home: Well-insulated homes retain cool air better, which means the AC doesn’t have to work as hard or take in as much electricity to maintain the desired temperature.
- The age and condition of the AC unit: Older AC units may not be as energy-efficient as newer models, and units that are not well-maintained may have issues that cause them to consume more electricity.
- The usage patterns: How often the AC is used and for how long can also affect energy consumption. For example, leaving the AC on all day when no one is home will result in unnecessary electricity usage.
By considering these factors and making informed choices, you can help optimize the energy consumption of your air conditioning system and reduce your electricity bills.
How does the size of the room impact energy usage?
The size of the room plays a crucial role in determining the energy usage of an air conditioner (AC). A larger room requires more electricity to cool down compared to a smaller room. This is because the AC unit needs to work harder and for a longer duration to reach the desired temperature in a larger space.
An AC unit installed in a small room can cool the space down relatively quickly, resulting in less electricity consumption. On the other hand, an AC unit in a larger room will take a longer time to cool the space, leading to more electricity consumption.
Additionally, larger rooms often have more insulation challenges. Due to the larger surface area, there may be more heat transfer from the surrounding environment, causing the AC unit to work harder to maintain the desired temperature. This increased workload further contributes to higher energy usage.
Moreover, when an AC unit is undersized for a particular room, it needs to run constantly to keep the temperature down, resulting in increased electricity consumption. Similarly, if an AC unit is oversized for a smaller room, it may cycle on and off too frequently, leading to energy wastage. Therefore, selecting the appropriately sized AC unit for the room is crucial to optimize energy usage.
In conclusion, the size of the room directly impacts the energy usage of an AC unit. A larger room requires more electricity to cool down due to increased workload and insulation challenges. Selecting the right-sized AC unit for the room can help minimize energy consumption and ensure efficient cooling.
| Small room | Low |
| Large room | High |
Does the brand of the air conditioner matter?
When it comes to electricity consumption, the brand of the air conditioner can indeed make a difference. While all air conditioners consume electricity to cool down a room, different brands may vary in terms of energy efficiency.
An energy-efficient air conditioner can take advantage of advanced technologies, such as variable-speed compressors or smart thermostats, to optimize its cooling performance while minimizing electricity usage. On the other hand, a less efficient air conditioner may consume more electricity to achieve the same cooling effect.
A study conducted by an independent testing agency found that certain brands of air conditioners were able to provide the same level of cooling while using less electricity compared to others. This means that investing in an energy-efficient air conditioner can save you money on your electricity bills in the long run.
It’s important to note that the energy efficiency of an air conditioner is often expressed through a metric called the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the air conditioner is. When comparing different brands, it’s advisable to look for units with a higher SEER rating.
| Brand A | 18 |
| Brand B | 16 |
| Brand C | 14 |
In the example table above, Brand A has the highest SEER rating of 18, indicating the highest energy efficiency among the three brands. Brand C has the lowest SEER rating of 14, suggesting that it may consume more electricity to achieve the same cooling effect.
Therefore, when considering purchasing an air conditioner, it’s worth researching and comparing different brands to find one that offers a good balance between energy efficiency and cooling performance. Investing in a higher-quality and energy-efficient air conditioner can pay off in terms of reduced electricity consumption and lower utility bills in the long run.
The role of energy efficiency ratings
Energy efficiency ratings play a crucial role in understanding the electricity consumption of air conditioners. With the increasing demand for cooling solutions, it is important to know how much electricity these AC units take up.
An energy efficiency rating is a measurement that indicates how efficiently an air conditioner can convert electricity into cooling output. This rating is typically represented by a number called the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) or Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER).
Higher energy efficiency ratings mean that the AC unit will require less electricity to cool the same space compared to units with lower ratings. Thus, a higher-rated AC unit will consume less electricity, leading to lower electricity bills in the long run.
When purchasing an air conditioner, it is wise to consider its energy efficiency rating to ensure that you are making an environmentally friendly and cost-effective choice. AC units with higher ratings may cost a bit more upfront but can save a lot of money on electricity bills over time.
It is important to note that energy efficiency ratings are not the only factor to consider when determining the electricity consumption of an AC unit. Other factors, such as the size of the space being cooled and the usage patterns, can also affect the amount of electricity consumed by an air conditioner.
In conclusion, energy efficiency ratings provide valuable information about the electricity consumption of an AC unit. By choosing an air conditioner with a high energy efficiency rating, consumers can save a lot of money on electricity bills while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Understanding SEER and EER
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) are two important measurements used to understand the energy efficiency of air conditioners.
The SEER rating of an air conditioner represents how efficiently it can cool a space over an entire cooling season. It is calculated by dividing the total cooling output of the AC unit over a typical cooling season, measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs), by the total electricity consumed by the unit during the same period, measured in watt-hours. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the air conditioner is.
The EER rating of an air conditioner, on the other hand, represents its energy efficiency under specific conditions. It is calculated by dividing the cooling capacity of the AC unit, measured in BTUs per hour, by the total electricity consumed by the unit in watts. Unlike SEER, EER does not take into account the seasonal variations in temperature, humidity, and usage patterns. A higher EER rating indicates better energy efficiency.
When choosing an air conditioner, it is important to consider both the SEER and EER ratings. A higher SEER or EER rating usually indicates a more energy-efficient unit, which can lead to lower energy bills and a reduced environmental impact. However, it is also important to consider the specific cooling needs of your space and climate to find the most suitable air conditioner.
How temperature settings affect energy consumption
When it comes to air conditioners (AC), the temperature settings you choose can have a significant impact on the electricity consumption of your unit. ACs are designed to cool down your space, but the lower you set the temperature, the more electricity it will consume.
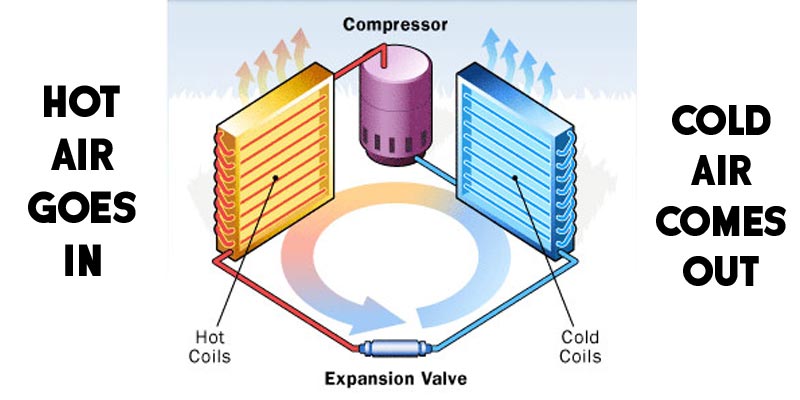
The reason for this is that air conditioners work by extracting heat from the air and expelling it outside, creating a cool and comfortable environment indoors. The lower the temperature setting, the harder the AC has to work to maintain that cool temperature.
So, if you set the temperature very low, the AC will run more frequently and for longer periods of time, consuming a lot of electricity in the process. On the other hand, if you set it at a moderate temperature, the AC will not have to work as hard, resulting in lower energy consumption.
It’s worth noting that the energy consumption of an AC can vary depending on factors such as the size of the unit, the insulation of your space, and the outdoor temperature. However, regardless of these variables, setting the temperature higher will always result in less electricity usage compared to a lower temperature setting.
It is recommended to set your AC to a temperature that is comfortable for you while still being energy-efficient. This can help reduce your overall electricity costs and lower your environmental impact.
Remember, finding the right balance between comfort and energy consumption is key when it comes to using your air conditioner efficiently.
The impact of insulation on electricity usage
Insulation plays a crucial role in the energy consumption of air conditioners. Without proper insulation, a significant amount of electricity can be wasted, leading to higher electricity bills and increased energy consumption.
So, how does insulation affect the electricity usage of an AC unit? Let’s take a closer look.
| Well-insulated | Takes a lot less electricity |
| Poorly insulated | Takes a lot more electricity |
A well-insulated air conditioner effectively prevents heat transfer between the indoors and outdoors. This means that the cool air generated by the AC unit remains inside, while the hot air from outside is kept out. As a result, the AC unit does not have to work as hard to maintain the desired temperature, leading to a significant reduction in electricity usage.
On the other hand, a poorly insulated air conditioner allows heat to easily penetrate through the walls, windows, and doors, resulting in the loss of cool air and the entry of hot air. In this case, the AC unit has to constantly run for longer periods and work harder to compensate for the heat gain, leading to a lot more electricity consumption.
Investing in proper insulation, such as insulating the walls, sealing the windows and doors, and using insulation materials, can greatly improve the energy efficiency of an air conditioner. With proper insulation, the AC unit can operate more efficiently, consume a lot less electricity, and provide better cooling comfort.
In conclusion, the insulation level of a building or room has a significant impact on the electricity usage of an air conditioner. A well-insulated space requires a lot less electricity for cooling, while a poorly insulated space demands a lot more. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to insulation and ensure that it is properly installed to maximize energy efficiency and reduce electricity bills.
Other features that can affect energy consumption
While the size and efficiency rating of an AC unit play a significant role in its energy consumption, there are other features that can also affect how much electricity it takes to run the unit.
One of these features is the presence of programmable settings. AC units that offer programmable timers and temperature presets allow users to set specific times for the unit to turn on or off, as well as pre-determined temperatures for different times of the day. By utilizing these settings, users can optimize their AC usage and avoid unnecessary energy consumption.
Another feature that can affect energy consumption is the presence of a sleep mode. Sleep mode adjusts the temperature and fan speed to provide a comfortable sleeping environment while minimizing energy usage. By allowing the AC unit to operate at a reduced capacity during the night, users can save on electricity without sacrificing their comfort.
In addition, some AC units come with smart connectivity options. These units can be controlled remotely through a smartphone or home automation system. This feature allows users to turn off the AC when they are away from home or easily adjust settings to conserve energy when needed.
Finally, the location and insulation of the AC unit can also impact its energy consumption. Units located in areas with proper insulation and good air circulation will require less electricity to maintain the desired temperature. On the other hand, if the unit is subjected to direct sunlight or placed in a poorly insulated area, it will have to work harder and consume more electricity.
By considering these additional features and their potential impact on energy consumption, consumers can make informed choices when selecting an AC unit that best fits their needs while minimizing their electricity usage.
Common misconceptions about air conditioner energy usage
There are several common misconceptions about the energy usage of air conditioners (AC). Many people believe that AC units consume a significant amount of electricity, causing their energy bills to skyrocket. However, this is not entirely true.
Firstly, it is important to understand that the energy consumption of an AC depends on various factors such as the size of the unit, the temperature set, the insulation of the room, and the outdoor conditions. A small AC unit in a well-insulated room will consume less electricity compared to a larger unit in a poorly insulated room.
Secondly, ACs use electricity to remove heat from indoor air and maintain a comfortable temperature. Contrary to popular belief, ACs do not create cool air but rather transfer heat from inside to outside. This means that the AC unit itself does not actually generate a lot of electricity, but instead, it uses electricity to remove the heat.
Another misconception is that leaving an AC running all day uses less electricity than turning it on and off. In reality, it is more energy-efficient to turn off the AC when you are not at home or if the room is already at a comfortable temperature. AC units are designed to cool a room down quickly, so it is better to use them strategically rather than leaving them on all day.
Lastly, some people believe that lowering the thermostat temperature will cool down the room faster. However, AC units cool at a consistent rate, regardless of the temperature setting. Lowering the temperature too much can lead to excessive energy usage without providing any additional benefits.
In conclusion, while air conditioners do consume electricity, the amount depends on various factors. Understanding how ACs work and debunking common misconceptions can help homeowners optimize their energy usage and potentially reduce their bills.
Comparing the energy consumption of different types of air conditioners
When it comes to cooling homes or buildings, electricity consumption is an important factor to consider. Air conditioners (AC) are the primary appliances used for this purpose, but not all AC units consume electricity at the same rate.
There are different types of AC units available, each with its own energy consumption characteristics. It is important to understand these differences to make an informed decision when choosing an air conditioner.
| Window AC | Takes up a moderate amount of electricity |
| Split AC | Consumes a moderate amount of electricity |
| Central AC | Uses a significant amount of electricity |
| Portable AC | Requires a moderate amount of electricity |
Window AC units are one of the most common types of air conditioners found in households. They typically consume a moderate amount of electricity compared to other types. Split AC units, which consist of indoor and outdoor components, also fall within the moderate energy consumption range.
Central AC systems, which are used for cooling large areas or entire buildings, demand a significant amount of electricity due to the high capacity needed for cooling such spaces. Portable AC units, on the other hand, generally require a moderate amount of electricity since they are designed for single-room cooling.
When considering energy consumption, it is important to note that individual AC units may vary in their efficiency. Energy-efficient models can significantly reduce electricity consumption while providing the same level of cooling as less efficient models.
In conclusion, understanding the energy consumption of different types of air conditioners is essential when making a choice. While all AC units consume electricity to provide cooling, some require more power than others. By considering factors such as the type of AC unit and its energy efficiency, you can optimize your cooling needs while minimizing electricity usage.
Tips for reducing air conditioner energy consumption
Taking steps to reduce the energy consumption of your air conditioner can have a significant impact on your electricity bill, as well as helping to lower your carbon footprint. Here are a few tips to consider:
1. Adjust the temperature: One of the simplest ways to reduce AC energy consumption is to set the thermostat at a higher temperature. A lot of energy is required to cool a space, so even increasing the temperature by a few degrees can make a noticeable difference.
2. Take advantage of natural ventilation: Instead of relying solely on your AC, try opening windows or using fans to circulate air. This can help to reduce the amount of time your AC needs to run, ultimately reducing energy consumption.
3. Seal gaps and cracks: Make sure your home is well-insulated by sealing any gaps or cracks around doors and windows. This will prevent cool air from escaping and hot air from entering, allowing your AC to work more efficiently.
4. Use shades or curtains: Direct sunlight can heat up a room quickly, causing your AC to work harder. Installing shades or curtains can help to block out the sun’s rays and keep your space cool, reducing energy consumption in the process.
5. Maintain your AC unit: Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring your AC operates efficiently. Clean or replace air filters as needed, and consider scheduling professional maintenance to keep your unit running at its best.
6. Use programmable thermostats: Programmable thermostats allow you to set different temperature settings throughout the day, adjusting based on when you are home or away. This can help to optimize energy usage and reduce AC consumption.
7. Consider using a fan: Fans use significantly less energy than air conditioners, and they can help to circulate cool air in a room. Using a combination of a fan and AC can allow you to dial back the AC temperature setting while maintaining comfort.
By implementing these tips, you can take control of your air conditioner’s energy consumption and make a positive impact on both your wallet and the environment.
Q&A:
How much electricity does an air conditioner use?
The electricity consumption of an air conditioner depends on various factors such as the size and efficiency of the unit, the temperature settings, and the usage patterns. On average, a typical residential air conditioner uses around 1,000 to 2,000 watts of electricity per hour of operation.
Do air conditioners consume more electricity than other household appliances?
Air conditioners typically consume more electricity compared to other household appliances due to their high power requirements. While the exact consumption varies, an air conditioner can use up to 3-4 times more electricity than a refrigerator and 10-15 times more electricity than a ceiling fan.
Are newer air conditioner models more energy-efficient?
Yes, newer air conditioner models are generally more energy-efficient compared to older ones. This is due to advancements in technology and stricter energy efficiency standards. Energy-efficient air conditioners use less electricity to provide the same cooling capacity, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower electricity bills.
How can I reduce the energy consumption of my air conditioner?
There are several ways to reduce the energy consumption of your air conditioner. First, you can ensure proper insulation and sealing of your home to minimize heat gain. Additionally, using ceiling fans in conjunction with your air conditioner can help distribute the cooled air more efficiently. Regular maintenance of your air conditioner, including cleaning or replacing filters, can also improve its efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Is it more energy-efficient to use a window air conditioner or a central air conditioner?
In general, a central air conditioner is more energy-efficient compared to a window air conditioner. Central air conditioners have more advanced technology and are designed to cool larger spaces, making them more efficient in terms of energy consumption. However, the energy efficiency also depends on factors such as the size of the area being cooled and the specific models of the air conditioners.