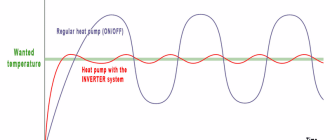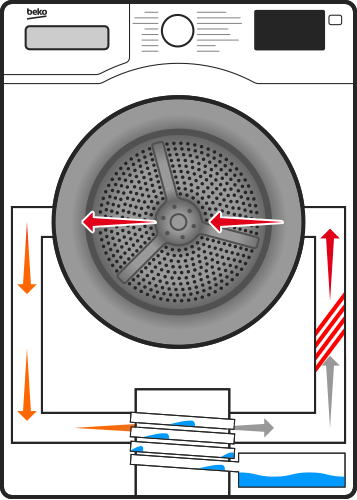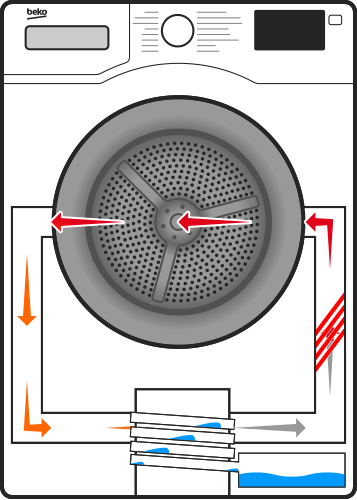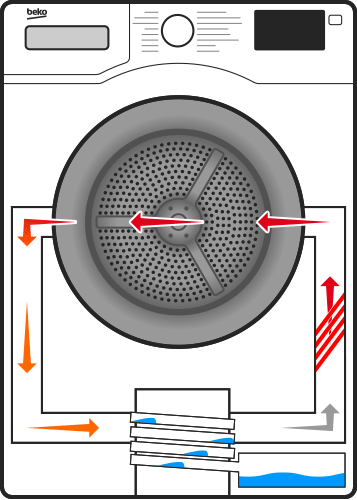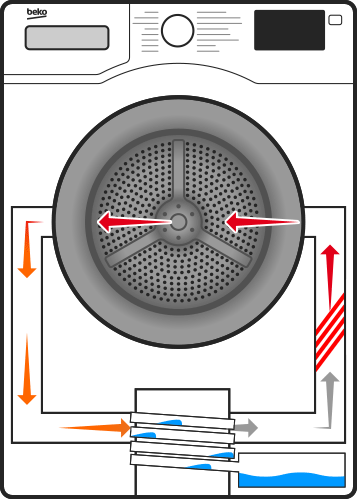
Heat Pump Condenser: Its Role and Common Problems
The heat pump condenser plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of a heat pump system. Whether used for heating or cooling, heat pumps have become a common choice for homeowners and businesses alike due to their energy efficiency and versatility. By transferring heat, rather than generating it, heat pumps can provide both warmth in the winter and cool air in the summer.
At the heart of every heat pump system lies the condenser. This component is responsible for releasing or absorbing heat depending on the desired temperature. During the winter months, the condenser extracts heat from the outdoor air and transfers it indoors, providing a comfortable and warm environment. In the summer, the process is reversed, with the condenser absorbing heat from the indoor air and releasing it outdoors, resulting in a cooling effect.
The key to the efficiency of a heat pump system is the condenser’s ability to effectively transfer heat. The condenser is equipped with a refrigerant, a substance that easily changes from a gas to a liquid and vice versa. As the refrigerant passes through the condenser, it undergoes a phase change, releasing or absorbing heat in the process. The heat exchange is facilitated by the condenser’s design, which maximizes the surface area for heat transfer.
It is important to note that the efficiency of a heat pump system heavily relies on the proper maintenance and operation of the condenser. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the condenser coils and ensuring proper refrigerant levels, can help optimize the performance and lifespan of the system. Additionally, keeping the area around the condenser clear of debris and obstructions will allow for proper airflow, further enhancing the system’s efficiency.
What is a Heat Pump Condenser?
A heat pump condenser plays a key role in the efficient operation of heating and cooling systems. It acts as a central component in both the heating and cooling processes, allowing heat to be transferred from one location to another.
The condenser is responsible for causing the refrigerant in the heat pump to undergo a phase change from a gas to a liquid state. This process releases heat energy, which is then used for heating purposes. In the cooling mode, the condenser helps remove heat from the indoor air, allowing the system to provide a comfortable cooling effect.
Common problems encountered with heat pump condensers include refrigerant leaks, faulty compressor motors, and clogged or dirty coils. These issues can lead to reduced efficiency, decreased heating or cooling capacity, and increased energy consumption. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, inspection, and prompt repairs, is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the condenser.
It is important to understand the role of the heat pump condenser in order to appreciate its significance in maintaining efficient heating and cooling. Without a properly functioning condenser, the heat pump system would not be able to effectively transfer heat, resulting in less efficient operation and potential comfort issues for the occupants of the space.
How does a Heat Pump Condenser work?
A heat pump condenser plays a crucial role in an efficient heating and cooling system. It is responsible for transferring heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. The condenser is a key component of the heat pump system, as it works in conjunction with the evaporator, compressor, and expansion valve to ensure effective heat transfer.
When the heat pump is in cooling mode, the condenser functions as a heat exchanger, releasing heat absorbed from the indoor air into the outdoor environment. The warm refrigerant from the evaporator coil flows into the condenser, where it is compressed by the compressor. This compression raises the temperature of the refrigerant, allowing it to release its heat into the outdoor air. The now-cooled refrigerant then returns to the indoor evaporator to repeat the cycle.
In heating mode, the heat pump operates in reverse, extracting heat from the outdoor air and transferring it indoors. The condenser plays a crucial role by absorbing heat from the outdoor air and releasing it into the indoor environment. This process is made possible by the refrigerant, which absorbs heat from the colder air outside and carries it indoors, where it is released through the condenser coils.
Although heat pump condensers are designed to be durable and efficient, they can encounter problems. One common issue is airflow restriction, which can occur due to dirt, leaves, or debris clogging the condenser coils. This can hinder heat transfer and reduce the overall efficiency of the heat pump system. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the condenser coils, is essential to prevent such issues and maintain optimal performance.
In summary, the heat pump condenser plays a vital role in the efficient operation of a heating and cooling system. It facilitates the transfer of heat between the indoor and outdoor environments, allowing for effective temperature control. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent common problems and ensure the condenser operates at its best.
| Key points: |
|---|
| – The heat pump condenser transfers heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. |
| – It works in conjunction with the evaporator, compressor, and expansion valve. |
| – In cooling mode, the condenser releases heat into the outdoor air. |
| – In heating mode, the condenser absorbs heat from the outdoor air and releases it indoors. |
| – Regular maintenance is essential to prevent common condenser problems. |
Efficiency of Heat Pump Condenser
The heat pump condenser plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency of a heat pump system. It is responsible for transferring heat from the indoors to the outdoors during the cooling mode and from the outdoors to the indoors during the heating mode. The condenser is designed to increase the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant gas, which allows it to release heat efficiently.
One of the common problems that can affect the efficiency of a heat pump condenser is a dirty or clogged condenser coil. When the condenser coil is covered in dirt, dust, or debris, it cannot effectively release heat, resulting in reduced efficiency and performance. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the condenser coil are essential to ensure optimal performance.
Another issue that can impact the efficiency of the heat pump condenser is refrigerant leaks. When there is a refrigerant leak, the heat pump system has to work harder to maintain the desired temperature, leading to increased energy consumption and decreased efficiency. It is important to address any refrigerant leaks promptly to prevent further damage to the condenser and improve the overall efficiency of the system.
In addition, airflow problems can also affect the efficiency of the heat pump condenser. Restricted airflow caused by blocked or dirty air filters, blocked vents, or obstructions around the outdoor unit can reduce the heat transfer process and decrease the efficiency of the system. Regularly checking and cleaning the air filters, keeping the outdoor unit clear of debris, and ensuring proper airflow are all important maintenance tasks to enhance the efficiency of the heat pump condenser.
- Regular cleaning and maintenance of the condenser coil are essential.
- Address refrigerant leaks promptly to improve efficiency.
- Check and clean air filters regularly to enhance airflow.
- Keep the outdoor unit clear of debris and obstructions.
By addressing these common problems and ensuring regular maintenance, the efficiency of the heat pump condenser can be optimized, resulting in improved heating and cooling performance and energy savings.
Energy Savings
One of the key factors in choosing a heat pump condenser is its role in energy savings. A heat pump condenser is a common component of an HVAC system that plays a crucial role in providing efficient heating and cooling. By leveraging the principle of heat transfer, a heat pump condenser extracts heat from the surrounding air or ground and transfers it inside a building during the winter months. In the summer, the process reverses, extracting heat from indoor air and transferring it outdoors to keep the building cool.
By utilizing this heat transfer process, heat pump condensers can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. They achieve this by not having to generate heat or cooling from scratch, but rather by extracting and transferring it. This results in lower energy bills and a reduced impact on the environment.
However, it is important to note that the efficiency of a heat pump condenser can be affected by a variety of common problems. These include inadequate insulation, duct leaks, improper installation, and improper sizing. It is important to address these issues promptly to ensure maximum energy savings and optimize the performance of the condenser.
Overall, a heat pump condenser is an essential component in an energy-efficient HVAC system. By properly maintaining and addressing any problems that arise, homeowners and businesses can enjoy the benefits of reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
Environmentally Friendly
When it comes to heating and cooling, an environmentally friendly option is always the best choice. The heat pump condenser plays a crucial role in making your HVAC system more sustainable and efficient.
Heat pumps are designed to transfer heat from one place to another, using minimal energy in the process. The condenser is a vital component of the heat pump system, responsible for releasing heat into the outside air during the summer and extracting heat from the outside air during the winter.
By utilizing the heat already present in the air, heat pump condensers avoid the need for burning fossil fuels, reducing harmful emissions that contribute to climate change. This makes them a greener alternative to traditional heating and cooling methods.
Furthermore, heat pump condensers help to address common environmental problems associated with HVAC systems. One common issue is the use of refrigerants that deplete the ozone layer. However, modern heat pump condensers utilize eco-friendly refrigerants that have a lower impact on the environment.
In addition, heat pump condensers can also help reduce the energy consumption of your HVAC system, leading to lower carbon emissions and a smaller carbon footprint. This can have a positive impact on the environment and help to conserve natural resources.
In summary, heat pump condensers play a crucial role in creating an environmentally friendly heating and cooling system. By utilizing the heat from the air and using eco-friendly refrigerants, they help reduce harmful emissions, conserve energy, and contribute to a healthier planet.
Benefits of Using a Heat Pump Condenser
A heat pump condenser plays a common and crucial role in the efficient operation of a heat pump system. It is an essential component that helps in both heating and cooling processes.
One of the main benefits of using a heat pump condenser is its ability to transfer heat energy from one location to another, making it an efficient solution for both heating and cooling needs. It can extract heat from the air, ground, or water source and then transfer it to the interior of a building during cold weather. Conversely, during hot weather, it can remove heat from the interior and transfer it to an outside area, effectively cooling the building.
In addition to its heating and cooling capabilities, a heat pump condenser also offers various advantages:
1. Energy Efficiency: A heat pump condenser is designed to be highly energy-efficient. It consumes less energy compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, resulting in lower energy bills.
2. Environmental Friendly: Heat pump condensers are an environmentally friendly choice as they use renewable energy sources, such as air, water, or ground, to operate. They produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions and have a lower carbon footprint.
3. Versatility: Heat pump condensers are versatile and can be used in various types of buildings, including residential homes, commercial spaces, and industrial facilities. They can also be installed in new constructions or retrofit into existing buildings.
4. Consistent Performance: A well-maintained heat pump condenser can provide consistent and reliable heating and cooling performance throughout the year, regardless of outside temperature fluctuations.
5. Minimized Space Requirement: Heat pump condensers are compact in size and generally require less space for installation compared to other heating and cooling systems. This makes them suitable for buildings with limited outdoor space.
Despite their numerous benefits, heat pump condensers are not without their problems. Common issues include refrigerant leaks, compressor failures, and airflow restrictions. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can help prevent these problems and ensure the longevity and efficiency of the heat pump condenser.
In conclusion, utilizing a heat pump condenser offers multiple benefits, including energy efficiency, environmental friendliness, versatility, consistent performance, and minimized space requirement. Understanding and addressing common problems can help maximize the benefits and functionality of this important component in heating and cooling systems.
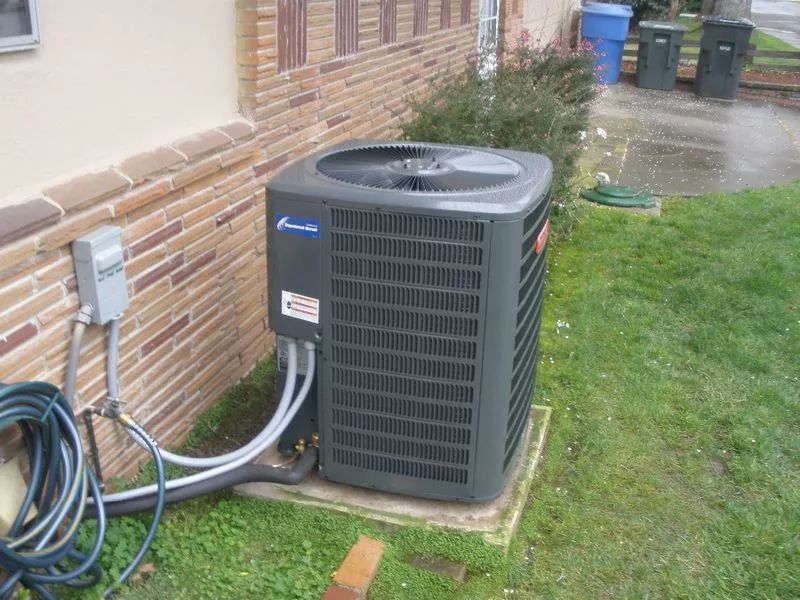
Cost Savings
One of the main advantages of using a heat pump condenser is the significant cost savings it can provide. The role of the heat pump condenser is to extract heat from the air and transfer it to the indoor space, providing both heating and cooling capabilities.
Compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, heat pump condensers are more energy-efficient, meaning they use less electricity to produce the same amount of heat or cooling. This can result in lower energy bills and reduced operating costs.
Another common way heat pump condensers save money is through their ability to provide both heating and cooling in one unit. Instead of having separate systems for heating and cooling, a heat pump condenser can do both, which eliminates the need for multiple units and reduces installation and maintenance costs.
Furthermore, heat pump condensers can take advantage of renewable energy sources, such as geothermal or solar power, for even greater cost savings. By using these sustainable energy sources, homeowners can reduce their reliance on traditional fossil fuels and further decrease their monthly energy expenses.
In summary, heat pump condensers offer cost savings through improved energy efficiency, combined heating and cooling capabilities, and the ability to utilize renewable energy sources. Investing in a heat pump condenser can lead to long-term financial benefits and a more sustainable home.

| Advantages of Heat Pump Condenser for Cost Savings: |
|---|
| Increased energy efficiency |
| Combined heating and cooling capabilities |
| Potential for renewable energy integration |
| Lower operating and installation costs |
Dual Functionality
The heat pump condenser plays a crucial role in both heating and cooling systems. Its dual functionality allows it to efficiently transfer heat to or from the surrounding air or water, depending on the desired temperature. This versatility makes heat pump condensers a popular choice for residential and commercial HVAC systems.
When used for heating, the heat pump condenser extracts heat from the outside air, even in cold temperatures, and transfers it indoors. This process is possible due to the refrigerant inside the condenser that absorbs the heat and evaporates at a low pressure. Once the hot refrigerant gas reaches the indoor coils, it releases the heat, and the now-cooled gas returns to the condenser to repeat the cycle.
On the other hand, during cooling mode, the heat pump condenser takes the heat from inside the building and releases it into the surrounding environment. It circulates the refrigerant to absorb the heat from the indoor coils and releases it outside through the condenser coils. The refrigerant condenses back into a liquid state, ready to repeat the cycle and cool the indoor space.
While the heat pump condenser offers significant energy efficiency and cost savings, it can encounter some common problems. One common issue is a faulty compressor, which can lead to reduced heating or cooling capacity. Another problem can be a refrigerant leak, which not only affects the performance but also poses environmental risks. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can help mitigate these issues and ensure the optimal functioning of the heat pump condenser.
In conclusion, the heat pump condenser’s dual functionality allows it to play a crucial role in both heating and cooling systems. By efficiently transferring heat between the indoor and outdoor environments, it provides energy-efficient and cost-effective climate control. However, it is important to address common problems and perform regular maintenance to ensure its optimal performance.
Long Lifespan
The heat pump condenser plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency of a heating and cooling system. One of the key advantages of a heat pump condenser is its long lifespan. With proper maintenance and care, a heat pump condenser can last for many years, providing reliable heating and cooling for your home.
Unlike traditional heating and cooling systems, heat pump condensers operate by transferring heat rather than generating it. This means that they are not subject to the common problems associated with combustion-based systems, such as worn-out components or inefficient fuel consumption.
In addition, heat pump condensers are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, including extreme temperatures and humidity levels. They are built with durable materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure their reliability. This makes them suitable for use in a wide range of environments, from arid desert climates to cold and snowy regions.
Regular maintenance is essential to prolonging the lifespan of a heat pump condenser. This includes cleaning or replacing the air filters, inspecting and lubricating the fan motor, and checking the refrigerant levels. By keeping up with these maintenance tasks, you can prevent common problems such as reduced efficiency, inadequate heating or cooling, and system breakdowns.
In conclusion, the heat pump condenser’s long lifespan is a major advantage that sets it apart from other heating and cooling systems. With proper care and maintenance, a heat pump condenser can provide efficient heating and cooling for many years, ensuring comfort and energy savings for your home.
Choosing the Right Heat Pump Condenser
When it comes to choosing a heat pump condenser, it is important to consider a few key factors to ensure the most efficient heating and cooling for your home. Common problems with heat pump condensers can result in reduced efficiency and performance, so it is crucial to select the right unit for your needs.
One of the first things to consider is the size of the heat pump condenser. It should be properly sized for your home, as an undersized or oversized unit can lead to problems. An undersized condenser may struggle to heat or cool your home adequately, while an oversized condenser may cycle on and off frequently, leading to increased wear and tear on the system.
Another important factor to consider is the type of heat pump condenser. There are different types available, including air source, ground source, and water source condensers. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to research and choose the one that best fits your specific needs and location.
You should also consider the energy efficiency of the heat pump condenser. Look for units with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings, as this indicates greater energy efficiency. A more efficient condenser can help to reduce your heating and cooling costs and contribute to a more sustainable home.
Lastly, it is important to consider the reliability and warranty of the heat pump condenser you choose. Look for reputable brands and models that offer reliable performance and have good customer reviews. Additionally, ensure that the condenser comes with a solid warranty to protect your investment and provide peace of mind.
By carefully considering these factors and choosing the right heat pump condenser for your home, you can ensure efficient heating and cooling and avoid common problems that may arise with an ill-suited unit.
Size
Choosing the right size for a heat pump condenser is crucial for its efficient operation. Many homeowners make the common mistake of selecting a condenser that is too big or too small for their heating and cooling needs.
When a heat pump condenser is too big, it tends to cool the space too quickly, resulting in short cycling. Short cycling refers to the pump turning on and off frequently, which can lead to excessive wear and tear on the system. It also puts unnecessary strain on the compressor and may increase energy usage.
On the other hand, if the heat pump condenser is too small, it may struggle to adequately heat or cool the space. This can lead to discomfort and inefficient operation, as the pump will have to work harder to maintain the desired temperature.
To determine the right size heat pump condenser for your home, it is essential to consider factors such as the square footage of the area to be heated or cooled, the insulation levels, and the climate. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can help ensure that you choose the right size for your home’s specific requirements.
In summary, sizing a heat pump condenser plays a crucial role in its overall efficiency and performance. Selecting the correct size can help prevent common problems such as short cycling, excessive energy usage, and inadequate heating or cooling. Trusting a professional to assess your specific needs is the best way to ensure that your heat pump condenser is properly sized for optimal operation.
Energy Efficiency Rating
The energy efficiency rating plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance of a heat pump condenser. This rating measures how effectively the condenser converts input energy into useful output heat. A higher energy efficiency rating indicates a more efficient system, which can result in significant energy savings.
One common problem that can lower the energy efficiency rating is improper installation. If the condenser is not installed correctly, it can lead to air leaks or inadequate airflow, reducing the system’s overall efficiency. Regular maintenance and inspections are necessary to ensure that the condenser is functioning optimally and that any issues are addressed promptly.
Another common problem that affects energy efficiency is the accumulation of dirt and debris on the condenser’s coils. When the coils are dirty, they cannot transfer heat effectively, causing the system to work harder and consume more energy. Regular cleaning of the condenser coils is crucial to maintain optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Furthermore, the energy efficiency rating can be influenced by the size of the condenser. A condenser that is too small for the heating or cooling needs of a space will have to work harder and consume more energy to reach the desired temperature. On the other hand, an oversized condenser may cycle on and off frequently, reducing efficiency and increasing energy consumption. Proper sizing of the condenser is essential to ensure optimal energy efficiency.
Overall, the energy efficiency rating of a heat pump condenser is an important factor to consider when selecting a system. By addressing common problems such as improper installation, dirt buildup, and sizing issues, homeowners can ensure that their condenser operates efficiently, saving energy and reducing utility costs.
Installation Requirements
Proper installation of a heat pump condenser is essential to ensure efficient heating and cooling in a residential or commercial setting. Here are some common installation requirements to consider:
- Location: The heat pump condenser should be installed in a location with adequate airflow and clearance. It should be placed on a stable, level surface away from obstructions and vegetation.
- Space: Sufficient space should be allocated for the heat pump condenser to allow for easy maintenance and repairs. The area around the unit should be clear of debris to prevent airflow restrictions.
- Piping: The condenser should be connected to the indoor unit via properly insulated refrigerant piping. The piping should be sized correctly and installed with proper slope and support to prevent condensation and potential leaks.
- Electrical Supply: A dedicated electrical circuit should be provided for the heat pump condenser. The electrical wiring should be installed by a qualified electrician and comply with local codes and regulations.
- Ductwork: The ductwork connected to the condenser should be properly designed and insulated to prevent air leakage and maximize efficiency. Any gaps or leaks in the ductwork should be sealed to avoid energy losses.
- Proper Sizing: It is important to properly size the heat pump condenser based on the heating and cooling load of the space. Oversized or undersized units can lead to problems such as reduced efficiency, inadequate cooling or heating, and increased energy consumption.
By following these installation requirements, you can ensure that your heat pump condenser operates at its optimal level, providing efficient heating and cooling for your space while minimizing common problems associated with improper installation.
Maintenance and Care
Maintaining and caring for your heat pump condenser is crucial to ensure its efficient performance and longevity. The condenser plays a key role in both heating and cooling your home, so regular maintenance is necessary to prevent common problems.
Cleaning: Regularly cleaning the condenser is essential to maintain its efficiency. Leaves, dirt, and debris can accumulate on the unit, obstructing airflow and reducing its performance. Use a garden hose to gently rinse off the condenser coil and remove any build-up.
Inspecting: Periodically inspect the condenser for any signs of damage or wear. Check for loose or damaged parts, such as fan blades or electrical connections, and replace them if necessary. Also, ensure that the fins on the condenser coil are not bent or damaged, as this can impede airflow.
Lubricating: Proper lubrication of the condenser’s moving parts is crucial for smooth operation. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to determine the type of lubricant to use and apply it as recommended. This will help reduce friction and extend the lifespan of the condenser.
Filter Replacement: The air filters in your heat pump play a vital role in maintaining indoor air quality and efficiency. Regularly replace or clean the filters to prevent them from becoming clogged with dust and debris. This will ensure proper airflow and prevent strain on the condenser.
Professional Maintenance: It is recommended to have a professional inspect and service your heat pump condenser at least once a year. They can conduct a thorough cleaning, check refrigerant levels, and identify any potential issues before they become major problems.
By following these maintenance and care tips, you can keep your heat pump condenser in optimal condition and enjoy efficient heating and cooling throughout the year.
Q&A:
What is a heat pump condenser and how does it work?
A heat pump condenser is a crucial component of a heat pump system that is responsible for transferring heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. It works by compressing and then expanding a refrigerant, which allows it to both absorb and release heat.
What are the benefits of using a heat pump condenser?
The use of a heat pump condenser offers several benefits, including increased energy efficiency, lower operating costs, and improved indoor air quality. Additionally, heat pump condensers are environmentally friendly, as they don’t rely on fossil fuels and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
Can a heat pump condenser be used for heating and cooling purposes?
Yes, a heat pump condenser can be used for both heating and cooling purposes. It can extract heat from the outdoor air during the winter and transfer it indoors to provide warmth. In the summer, it can extract heat from the indoor air and release it outdoors, thus providing cooling.
Is it necessary to have a heat pump condenser in a heat pump system?
Yes, a heat pump condenser is an essential component of a heat pump system. Without a condenser, the heat pump system would not be able to transfer heat effectively between the indoor and outdoor environments, resulting in inefficient heating and cooling.
Do heat pump condensers require regular maintenance?
Yes, heat pump condensers require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This may include cleaning or replacing air filters, inspecting and cleaning the condenser coils, checking refrigerant levels, and lubricating moving parts. Regular maintenance can help extend the lifespan of the condenser and prevent issues.
What is a heat pump condenser?
A heat pump condenser is a component of a heat pump system that is responsible for transferring heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. It acts as the outdoor unit of the heat pump and is essential for the efficient heating and cooling of a building.
How does a heat pump condenser work?
A heat pump condenser works by utilizing a refrigerant to transfer heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. In heating mode, the condenser extracts heat from the outdoor air, even when the temperature is low, and transfers it to the indoor air. In cooling mode, the process is reversed, with the condenser extracting heat from the indoor air and releasing it to the outdoor environment.