Heat Pump vs. Furnace: Which One Works Best?
When it comes to heating our homes, we are often faced with the decision between a heat pump and a furnace. Both of these systems have their own pros and cons, but which one is the best choice for your home? In this article, we will compare the efficiency, cost, and performance of these two heating options to help you make an informed decision.
Firstly, let’s look at the efficiency of a heat pump vs. a furnace. A heat pump is known for its energy efficiency, as it works by transferring heat from one area to another, rather than generating heat itself. This makes it an excellent choice for moderate climates, where the temperature rarely drops below freezing. On the other hand, a furnace is specifically designed to generate heat, making it a more suitable option for colder climates.
Next, let’s talk about the cost of these heating systems. Generally, heat pumps tend to have a higher upfront cost compared to furnaces. However, when it comes to long-term savings, a heat pump can be more cost-effective due to its energy-efficient operation. Additionally, heat pumps can also provide cooling during the summer months, further increasing their value for money.
Lastly, let’s consider the performance of a heat pump vs. a furnace. A heat pump provides consistent heating throughout your home, as it evenly distributes warm air. It also has the advantage of being able to operate all year round, making it a versatile option. On the other hand, a furnace can provide high heat output, making it a faster and more powerful heating option.
In conclusion, the choice between a heat pump and a furnace depends on various factors such as climate, budget, and personal preferences. A heat pump is more energy-efficient and cost-effective in the long run, while a furnace offers higher heat output and is better suited for colder climates. Ultimately, it is essential to consider your specific needs and consult with a professional to determine which heating system will work best for you.
Energy Efficiency: A Key Factor in Choosing Between a Heat Pump and a Furnace
When it comes to heating your home, energy efficiency is a crucial factor to consider. Both a heat pump and a furnace are popular options for residential heating, but they have different levels of energy efficiency.
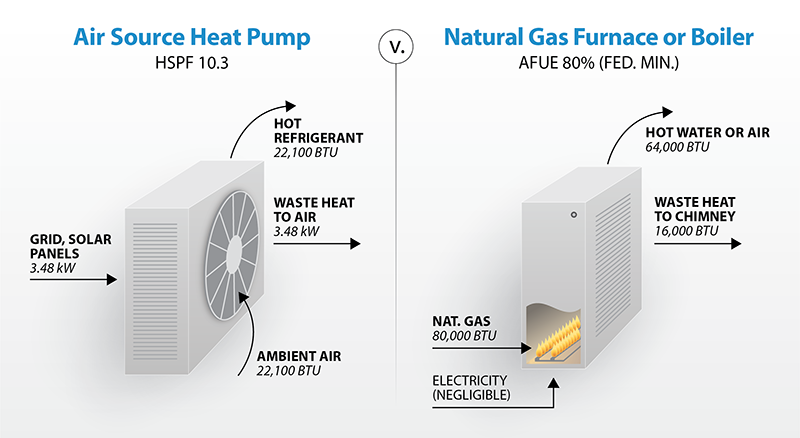
Heat pumps are known for their high energy efficiency. Unlike furnaces, which generate heat by burning fuel, heat pumps work by transferring heat from the outdoor air or ground into the home. This process consumes less energy compared to generating heat from scratch, making heat pumps a more environmentally friendly choice. In fact, heat pumps can provide up to four times more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume.
On the other hand, furnaces are powered by electricity, oil, or natural gas. While modern furnaces have become more efficient in recent years, they still fall short of the efficiency levels achieved by heat pumps. Furnaces typically offer an energy efficiency rating known as the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) percentage, which indicates how much energy is converted into usable heat. The higher the AFUE percentage, the more efficient the furnace.
So, which one is the best option? It ultimately depends on your specific needs and circumstances. If you live in a moderate climate and prioritize energy efficiency, a heat pump may be the better choice. On the other hand, if you live in a colder climate and prefer a heating system that can provide maximum warmth, a furnace may be more suitable.
It’s also worth noting that heat pumps can serve a dual purpose by providing both heating and cooling, whereas furnaces only provide heating. This versatility may be a deciding factor for some homeowners.
In summary, energy efficiency is a key factor when choosing between a heat pump and a furnace. Heat pumps are known for their high efficiency levels, while furnaces offer varying levels of efficiency depending on the model and fuel source. Consider your specific needs and climate to determine which option is best for you.
Cost Considerations: Examining the Financial Implications of a Heat Pump and a Furnace
When considering the cost of heating your home, it’s important to examine the financial implications of both a heat pump and a furnace. Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the cost differences can help you make an informed decision.
A heat pump, which works by extracting heat from the air or ground and transferring it into your home, is generally more energy-efficient than a furnace. This means that a heat pump can provide the same amount of heat while using less energy, resulting in lower heating costs. Additionally, heat pumps can also be used for cooling your home during hot summer months, providing added value.
On the other hand, a furnace is typically less expensive to purchase and install compared to a heat pump. However, it may not be as efficient as a heat pump and can have higher operating costs in the long run. Furnaces rely on burning fuel to generate heat, which can result in higher energy bills. Additionally, maintenance and repair costs for furnaces can also be higher compared to heat pumps.
When comparing the cost of a heat pump versus a furnace, it’s important to consider the lifespan of each system. While a heat pump may have a higher upfront cost, it often has a longer lifespan than a furnace. This means that the initial investment in a heat pump can be spread out over a longer period of time, potentially resulting in lower overall costs.
Another factor to consider is the availability of incentives and rebates for installing energy-efficient systems. In some areas, homeowners may be eligible for tax credits or other financial incentives for choosing a heat pump over a furnace. These savings can further offset the initial cost difference between the two systems.
In conclusion, when it comes to cost considerations, a heat pump can provide long-term energy savings and potential incentives, but may have a higher upfront cost. On the other hand, a furnace may be more affordable initially, but can lead to higher operating costs. It’s important to weigh the financial implications and consider your specific heating needs and budget before deciding which option works best for you.
Heating Performance: Assessing the Heat Output and Effectiveness of a Heat Pump vs. a Furnace
When it comes to heating your home, choosing the best system that works for you is crucial. Two popular options are heat pumps and furnaces, each offering their own benefits and drawbacks. One important factor to consider when comparing these two options is their heating performance, specifically the heat output and effectiveness.
A heat pump is designed to extract heat from the outside air or the ground and transfer it inside your home. It works by using a refrigeration cycle that absorbs heat from a cold source and releases it at a higher temperature. This process allows the heat pump to provide warmth even in colder temperatures. However, the effectiveness of a heat pump can be affected by extremely cold weather, as the temperature differential between the outside air and desired indoor temperature becomes smaller and the heat exchanger has to work harder to extract heat.
On the other hand, a furnace heats your home by burning fuel, such as natural gas, propane, or oil, to generate heat. A combustion process takes place within the furnace, producing hot air that is then distributed throughout your home. Unlike a heat pump, a furnace does not rely on external temperature conditions and can provide consistent heat regardless of outdoor temperatures.
When comparing the heat output of a heat pump vs. a furnace, it is important to consider factors such as efficiency and cost. Heat pumps are known for their high efficiency, as they can produce more heat energy than the electricity used to power them. Furnaces can also provide efficient heating, with newer models incorporating advanced technologies to maximize energy efficiency.
Ultimately, the best option for heating your home depends on various factors, including climate, energy costs, and personal preferences. If you live in an area with moderate winter temperatures, a heat pump may be a cost-effective and energy-efficient choice. However, if you reside in an extremely cold climate, a furnace might be a more reliable option to ensure consistent and effective heating.
| Heat Output | Relies on extracting heat from the outside air or ground | Burns fuel to generate heat |
| Effectiveness | Efficient in moderate temperatures, less effective in extreme cold | Consistently provides heat regardless of outdoor temperatures |
| Efficiency | Produces more heat energy than the electricity used | Newer models offer high energy efficiency |
| Cost | Lower operating costs due to high efficiency | May require higher upfront and operating costs, depending on fuel prices |
In conclusion, both heat pumps and furnaces have their advantages and limitations in terms of heating performance. It is essential to evaluate your specific heating needs and consider factors such as climate, energy costs, and personal preferences to determine which option will work best for your home.
Cooling Performance: Understanding the Cooling Capabilities of a Heat Pump Compared to a Furnace
When it comes to cooling your home, you have a few options to consider. Two of the most popular choices are heat pumps and furnaces. While both of these systems can provide some level of cooling, it’s important to understand their capabilities to make the best choice for your needs.
A heat pump is a versatile system that can both heat and cool your home. It works by extracting heat from the air inside your home and transferring it outside in warm months, effectively cooling the indoors. The heat pump uses a refrigerant to absorb and release heat, making it an efficient cooling solution.
On the other hand, a furnace primarily provides heating rather than cooling. It works by burning fuel to generate heat, which is then distributed throughout your home via ducts. While some furnaces come with an integrated air conditioning unit, they tend to be less efficient at cooling compared to heat pumps.
When comparing the cooling capabilities of a heat pump versus a furnace, it is clear that the heat pump is the better option. Not only does it provide both heating and cooling, but it does so with higher energy efficiency. This means that you can enjoy a comfortable indoor temperature while also reducing your energy consumption and utility bills.
In conclusion, if you are looking for a system that can efficiently cool your home, a heat pump is the way to go. Its ability to provide both heating and cooling, along with its energy efficiency, make it a desirable choice over a furnace. Consider your specific needs and budget to determine which option is best for you.
Renewable Energy: Exploring the Potential Benefits of a Heat Pump in Utilizing Renewable Energy Sources
When it comes to utilizing renewable energy sources, heat pumps are one of the best options available. A heat pump works by transferring heat from one area to another, rather than generating heat itself. This makes it highly efficient and environmentally friendly compared to traditional furnaces.
Unlike furnaces, which burn fuel to produce heat, heat pumps extract heat from the air, ground, or water. This means that they can utilize renewable energy sources such as air and geothermal heat, making them a sustainable choice for heating and cooling needs.
One of the key benefits of heat pumps is their high efficiency. They can provide up to four times as much heat energy as the electrical energy they consume, resulting in significant energy savings. This not only reduces utility bills but also helps to decrease the demand for non-renewable energy sources.
In addition to their energy efficiency, heat pumps are also known for their versatility. They can be used for both heating and cooling purposes, meaning that they offer year-round comfort. By reversing the refrigeration cycle, a heat pump can absorb heat from the ambient air and release it indoors during colder months. In warmer months, the process is reversed to provide cooling.
Another advantage of heat pumps is their long lifespan and low maintenance requirements. With regular maintenance, a heat pump can last for 20 years or more, making it a durable and cost-effective investment. In contrast, furnaces typically have a lifespan of around 15 years and require more frequent maintenance and repairs.
Overall, heat pumps offer numerous benefits when it comes to utilizing renewable energy sources. Their efficiency, versatility, and long lifespan make them a reliable and eco-friendly choice for heating and cooling needs. Whether it’s in a residential or commercial setting, a heat pump can help to reduce carbon emissions and decrease reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to a greener future.
Fuel Source Options: Comparing the Different Types of Fuels Used by Heat Pumps and Furnaces
When it comes to choosing between a heat pump and a furnace, one of the key factors to consider is the fuel source. Both heat pumps and furnaces use different types of fuels to provide heat in a home or building. Understanding the differences between these fuel sources can help you decide which option works best for your needs.
Heat pumps are typically powered by electricity, making them an efficient and environmentally friendly choice. They work by transferring heat from the outside air or ground into your home, providing both heating and cooling capabilities. This means that heat pumps rely on the availability and cost of electricity to function. While electricity is a readily available fuel source, it can be more expensive than other options in some areas.
Furnaces, on the other hand, can be powered by a variety of fuels including natural gas, oil, and propane. Natural gas is the most common fuel source for furnaces, as it is usually cheaper and more readily available than other options. Oil and propane are alternative fuel sources that may be used in areas where natural gas is not readily available. Furnaces burn these fuels to generate heat, which is then distributed throughout the home via ductwork.
The choice between a heat pump and a furnace ultimately depends on your specific needs and circumstances. If you have access to affordable electricity, a heat pump may be the most cost-effective and efficient option for you. On the other hand, if you have access to natural gas or other affordable fuel sources, a furnace may be a better choice.
It is also worth noting that some homes or buildings may benefit from a combination of both a heat pump and a furnace, known as a dual fuel system. This allows the heat pump to provide heating and cooling during mild weather conditions, while the furnace takes over during colder periods, when the heat pump may struggle to extract sufficient heat from the air or ground.
In conclusion, comparing the different types of fuels used by heat pumps and furnaces is an important step in determining which option works best for your heating needs. Consider factors such as fuel availability, cost, and efficiency to make an informed decision.
Environmental Impact: Considering the Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Heat Pumps and Furnaces
When it comes to choosing between a furnace and a heat pump, one important factor to consider is their environmental impact. Greenhouse gas emissions are a major concern in today’s world, and selecting the best heating option can help reduce our carbon footprint.
A furnace works by burning fuel, such as natural gas or oil, to generate heat. This combustion process releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases contribute to global warming and climate change. The amount of emissions produced by a furnace depends on its efficiency and the type of fuel used.
In comparison, a heat pump operates by transferring heat from one place to another, rather than burning fuel. Heat pumps use electricity to extract heat from the outside air or ground and deliver it inside. While a heat pump still requires electricity to function, it can be more energy-efficient than a furnace.
Because heat pumps do not burn fuel, they produce significantly fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to furnaces. The reduced emissions make heat pumps a more environmentally friendly heating option. However, it’s important to note that the environmental impact of a heat pump also depends on how the electricity is generated. If the electricity comes from coal-fired power plants, the overall emissions from a heat pump may still be higher than desired.
To ensure the greenest heating option, it is recommended to choose a heat pump powered by renewable energy sources or opt for a high-efficiency furnace that minimizes emissions. Investing in insulation and weatherization can also improve the efficiency of both heating systems, reducing the overall energy consumption and emissions.
In conclusion, when considering the environmental impact of heat pumps and furnaces, heat pumps have the advantage of producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions. However, the source of electricity used to power a heat pump also plays a significant role in determining its overall environmental impact. Making sustainable energy choices and improving the energy efficiency of our homes are essential steps towards reducing our carbon footprint.
Lifespan and Maintenance: Evaluating the Longevity and Maintenance Requirements of Heat Pumps vs. Furnaces
When considering the lifespan and maintenance requirements of heating systems, it is important to evaluate both heat pumps and furnaces to determine which option works best for your needs.
Heat pumps and furnaces have different lifespans. On average, a heat pump can last anywhere from 15 to 20 years, while a furnace typically has a lifespan of around 15 to 30 years. This means that if longevity is a top priority for you, a furnace may be the better option.
In terms of maintenance, heat pumps require regular upkeep to ensure optimal performance. This includes tasks such as replacing filters, cleaning coils, and inspecting electrical connections. Furnaces also require maintenance, but typically not as frequently as heat pumps. Regular maintenance for furnaces includes cleaning or replacing filters, inspecting burners, and checking for any leaks or cracks in the heat exchanger.
It is worth noting that the maintenance requirements for both heat pumps and furnaces can vary depending on factors such as climate, usage, and manufacturer recommendations. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can help you determine the specific maintenance needs for your system.
In conclusion, when evaluating the lifespan and maintenance requirements of heat pumps vs. furnaces, it is important to consider factors such as longevity and regular upkeep. While a heat pump may have a shorter lifespan compared to a furnace, it requires more frequent maintenance. Ultimately, the best choice for your home will depend on your specific needs and priorities.
Installation Considerations: Understanding the Installation Processes and Requirements for Heat Pumps and Furnaces
When it comes to installing a heating system in your home, it’s important to understand the installation processes and requirements for both heat pumps and furnaces. This will help you make an informed decision about which option is best for your specific needs.
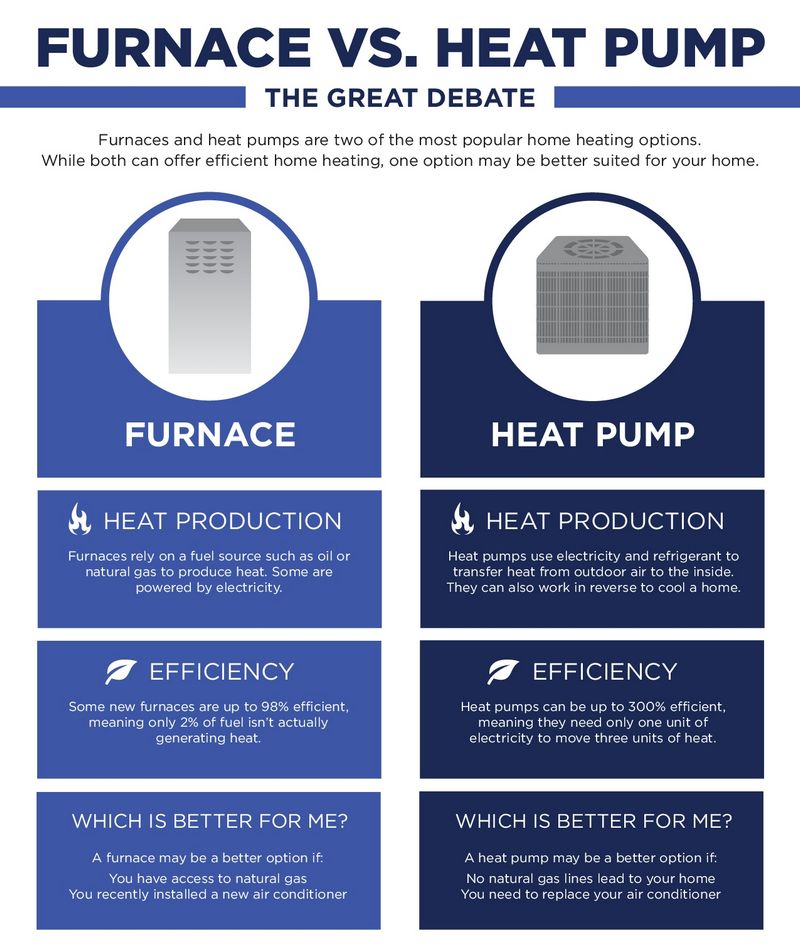
One of the major differences between heat pumps and furnaces is the way they generate heat. While a furnace relies on burning fuel to produce heat, a heat pump uses electricity to transfer heat from the air or ground into your home. This distinction affects the installation process and requirements for each system.
When installing a heat pump, several factors come into play. The location of the outdoor unit is crucial, as it needs to be placed where it can efficiently extract heat from the air or ground. It’s also important to consider the size and layout of your home to determine the capacity and number of indoor units needed for optimal heating and cooling.
Furthermore, proper insulation and sealing are essential to ensure the heat pump operates efficiently. If there are any air leaks or insufficient insulation, the heat pump may have to work harder to maintain the desired temperature, leading to increased energy consumption and reduced efficiency.
Installing a furnace involves its own set of considerations. Since furnaces produce heat by burning fuel, proper ventilation and exhaust systems are essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the unit. This may require additional modifications to your home’s existing ductwork and ventilation system.
In addition, the type of fuel used by the furnace will also affect the installation process. Gas furnaces require a gas line connection, while oil furnaces need an oil storage tank and delivery system. These requirements should be carefully assessed to determine the feasibility and cost of installing a furnace in your home.
Ultimately, the decision between a heat pump and a furnace will depend on several factors including your climate, energy costs, and personal preferences. Understanding the installation processes and requirements for each system can help you make an informed choice about which one is best suited for your home.
Whether you opt for a heat pump or a furnace, it is recommended to hire a professional HVAC technician for the installation. They have the necessary expertise and experience to ensure a proper and efficient installation that will keep your home warm and comfortable throughout the year.
Space Requirements: Assessing the Space Needed for Heat Pumps vs. Furnaces
When it comes to considering the space requirements for heat pumps vs. furnaces, various factors must be taken into account. The size of the units, including both the indoor and outdoor components, is a crucial consideration.
Heat pumps typically require less space compared to furnaces. This is because heat pumps have both an indoor and outdoor unit, but their sizes are generally smaller than furnaces. The indoor unit of a heat pump is typically compact and can be installed on the wall or ceiling, while the outdoor unit is placed outside the home.
On the other hand, furnaces are usually larger and require more space for installation. They have a single unit that is typically installed in a basement, attic, or dedicated utility room. The size of a furnace can vary depending on the heating capacity required for the home, but they are generally larger than heat pump units.
When comparing space requirements, it is essential to consider the available space in your home. If you have limited space, a heat pump may be a better option since it requires less room for installation. However, if you have a spacious basement or utility room, a furnace may be more suitable.
Ultimately, the choice between a heat pump and furnace depends on various factors, including the available space, efficiency, cost, and performance. Consulting with a heating and cooling professional can help you determine which option is best for your specific needs and space requirements.
Noise Levels: Comparing the Operation Noise of Heat Pumps and Furnaces
When deciding between a heat pump and a furnace, one important factor to consider is the noise level of the operation. No one wants a heating system that disrupts their daily activities or disturbs the peace and quiet of their home environment. Let’s take a closer look at how heat pumps and furnaces compare in terms of noise levels.
Heat Pumps: Heat pumps are known for their quiet operation. They typically produce a noise level of around 50 decibels, which is comparable to a normal conversation or background music. This makes them a great choice for homeowners who value a peaceful and quiet living environment.
Furnaces: On the other hand, furnaces can be noisier compared to heat pumps. While newer models are designed to reduce noise levels, they can still produce sounds of up to 60 decibels. This noise level is similar to the sound of a dishwasher or an air conditioning unit. It’s important to note that older furnaces may be even louder.
Which One Works Best for You?
Ultimately, the choice between a heat pump and a furnace depends on your personal preferences and priorities. If noise levels are a key concern for you, a heat pump may be the better option. However, if noise is not a major factor and you prioritize other aspects such as cost or energy efficiency, a furnace might be the right choice for you.
When making your decision, it’s also important to consider the location of the heating system. If it will be placed near living areas or bedrooms, a quieter option like a heat pump may be more suitable. However, if the system will be installed in a basement or utility room, the noise level might not be as much of a concern.
In conclusion, heat pumps generally offer a quieter operation compared to furnaces. However, it’s crucial to evaluate all factors and make an informed decision based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Home Comfort: Examining the Temperature Control and Convenience of Heat Pumps and Furnaces
When it comes to heating your home, there are two main options to consider: a heat pump or a furnace. Both of these systems have their strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to understand the differences and determine which one is best for your home.
One of the key factors to consider when comparing a heat pump vs. a furnace is temperature control. Heat pumps are known for their ability to both cool and heat a home, making them a versatile choice. With a heat pump, you can easily adjust the temperature to your desired level, ensuring that your home is always comfortable.
On the other hand, furnaces are specifically designed for heating only. While they may not offer the cooling function of a heat pump, furnaces are known for their ability to quickly and efficiently warm up a home. This can be particularly beneficial in cold climates where heating is a major priority.
Convenience is another important aspect to consider. Heat pumps are generally easier to install and require less maintenance compared to furnaces. They are also more energy-efficient, which can result in lower energy bills. However, heat pumps may not be as effective in extremely cold temperatures, as their efficiency tends to decrease in such conditions.
Meanwhile, furnaces tend to be more reliable in colder climates and can quickly heat up a home even when temperatures drop significantly. They may require more regular maintenance and have higher energy consumption compared to heat pumps, but their performance in extreme cold weather can be a major advantage.
- In summary, when it comes to temperature control and convenience, heat pumps provide the advantage of both heating and cooling capabilities, making them a versatile choice. They are easier to install, more energy-efficient, and require less maintenance. However, in extremely cold climates, a furnace may be the best option due to its reliability and ability to quickly heat up a home.
- Ultimately, the decision between a heat pump and a furnace depends on your specific needs and climate. It’s always best to consult with a professional to determine which system is the right fit for your home.
Climate Considerations: Identifying the Best Heating and Cooling System for Different Climate Zones
When it comes to heating and cooling your home, it’s important to choose the right system that best fits the climate zone you live in. Both heat pumps and furnaces are popular options, but understanding how each works and which one is more suitable for your specific climate is crucial.
A heat pump is a versatile heating and cooling system that can extract heat from the air or ground, depending on the type of pump. It works by transferring heat from one place to another, making it an energy-efficient option for both heating and cooling. However, its performance can be affected in extreme climates with extremely low or high temperatures.
On the other hand, a furnace is a traditional heating system that uses fuel combustion, typically natural gas, to generate heat. It generally works well in colder climates, as it can provide a high level of heat output and effectively warm up a home quickly. However, it doesn’t have the ability to cool a home, so additional cooling systems may be required in warmer climates.
So, which one is the best heating and cooling system for different climate zones? Let’s take a look at some common climate zones and their suitability for heat pumps and furnaces:
| Mild or Temperate | Works well | May not be necessary |
| Cold | Can still work, but may need supplemental heat source | Works well |
| Very cold | May not be suitable without supplemental heat source | Works well |
| Hot | Works well | May not be necessary |
In mild or temperate climate zones, heat pumps can work effectively and efficiently for both heating and cooling, making them a popular choice. Furnaces may not be necessary in these zones, as the temperature variations are not extreme.
In colder climate zones, both heat pumps and furnaces can work well. However, heat pumps may need a supplemental heat source in extremely cold temperatures, while furnaces can provide consistent and reliable heat output.
For very cold climate zones, heat pumps may not be suitable without a supplemental heat source, as the extremely low temperatures can affect their performance. Furnaces, on the other hand, work well even in these conditions and can provide the necessary heat to keep a home warm.
In hot climate zones where cooling is more important than heating, both heat pumps and furnaces may not be necessary. Other cooling systems, such as air conditioners or evaporative coolers, may be more suitable.
In conclusion, choosing the best heating and cooling system for different climate zones depends on factors like temperature extremes, energy efficiency, and the need for cooling. Heat pumps are generally a versatile choice, while furnaces are more suitable for colder climate zones. Understanding your specific climate zone and its requirements will help you make an informed decision.
Government Incentives: Discovering Potential Financial Incentives for Installing a Heat Pump or Furnace
When it comes to deciding between a heat pump and a furnace, one of the key factors to consider is the potential financial incentives offered by the government. These incentives can help offset the initial costs of installation and make one option more appealing than the other.
So, which option is the best when it comes to receiving government incentives? Let’s explore.
Heat pumps:
- Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, and this makes them eligible for several government incentives aimed at promoting renewable energy sources.
- Depending on where you live, you may be eligible for federal tax credits or rebates when you install a heat pump.
- In addition, some states offer their own incentives, such as grants or low-interest loans, to further encourage the adoption of heat pumps.
Furnaces:
- Furnaces are not typically as energy efficient as heat pumps, but there are still potential financial incentives available for installing a furnace.
- Similar to heat pumps, federal tax credits and rebates may be available for eligible furnace installations.
- Some local utility companies also offer rebates or discounts for choosing a high-efficiency furnace.
Ultimately, the best option in terms of government incentives will depend on various factors, such as your location and the specific programs available in your area. It is recommended to research and consult with local authorities or energy efficiency organizations to understand the potential financial incentives for both heat pumps and furnaces in your region.
In conclusion, when considering the installation of a heat pump or furnace, it is important to take into account the potential financial incentives provided by the government. This information can help you make an informed decision about which option works best for you in terms of cost and overall performance.
Q&A:
What is the difference between a heat pump and a furnace?
A heat pump and a furnace are both types of heating systems, but they operate differently. A heat pump uses electricity to transfer heat from the outside air or ground to the inside of a building, while a furnace generates heat by burning fuel, such as natural gas or oil.
Which is more efficient: a heat pump or a furnace?
A heat pump is typically more efficient than a furnace. Heat pumps can achieve higher efficiency ratings because they transfer heat rather than generate it, using less energy in the process. However, the efficiency of both systems can vary depending on factors such as climate and installation.
What are the pros and cons of a heat pump?
Some advantages of a heat pump include higher efficiency, the ability to provide both heating and cooling, and lower operating costs. However, heat pumps may struggle to heat a home in extremely cold climates and may require a backup heating system. Additionally, heat pump installation costs can be higher than those of a furnace.
What are the pros and cons of a furnace?
One advantage of a furnace is its ability to provide a high level of heat in any climate, making it a reliable option for colder regions. Furnaces also tend to have lower upfront installation costs compared to heat pumps. However, furnaces can be less efficient and more expensive to operate, especially if the price of fuel is high.
Which is more cost-effective: a heat pump or a furnace?
The cost-effectiveness of a heat pump or a furnace depends on various factors, such as the climate, energy prices, and the efficiency of the system. In general, a heat pump is more cost-effective in milder climates with lower electricity prices, while a furnace may be more cost-effective in colder climates with lower fuel prices. It is important to consider both upfront installation costs and long-term operating costs when determining cost-effectiveness.
What is a heat pump and how does it work?
A heat pump is a device that uses refrigerant to transfer heat from one place to another, typically from outside to inside. It works by extracting heat from the air or ground and then transferring it to the inside of a building. It can also be used in reverse to cool a building by extracting heat from inside and transferring it outside.
What is a furnace and how does it work?
A furnace is a heating system that uses fuel combustion, such as natural gas or oil, to create heat. It usually consists of a burner that ignites the fuel, a heat exchanger that transfers the heat to the air, and a blower that circulates the warm air throughout the building. The combustion process creates hot gases that are vented out of the building.






