A Guide to Gas Furnace Efficiency: Decoding and interpreting various ratings
When it comes to deciding on a gas furnace for your home, understanding the different ratings and what they mean is crucial. The efficiency of a furnace can have a significant impact on energy consumption and ultimately your monthly utility bills. But how do you make sense of all the ratings and what do they really mean? Let’s break it down.
Firstly, it’s important to note that there are different ratings used to measure the efficiency of a gas furnace. One of the most commonly used ratings is the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE). This rating measures the amount of heat produced by the furnace compared to the amount of energy consumed. A higher AFUE rating indicates a more efficient furnace, which means it will produce more heat for every unit of fuel consumed.
In addition to the AFUE rating, there are also other ratings to consider. The Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) measures the efficiency of the furnace’s heat pump in heating mode, while the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) measures the efficiency of the furnace’s cooling system. These ratings are important if you’re looking for a furnace that can also provide cooling during the warmer months.
Understanding these ratings is essential when choosing a gas furnace for your home. Higher efficiency ratings can save you money in the long run by reducing your energy consumption, but they may come with a higher upfront cost. It’s important to find the right balance between efficiency and cost, taking into consideration your specific heating needs and budget.
What is a Gas Furnace Efficiency Rating?
Understanding gas furnace efficiency ratings is important when choosing a furnace for your home. The efficiency rating of a gas furnace refers to how effectively it converts fuel into heat. This rating is expressed as a percentage and can vary depending on the model and manufacturer.
Gas furnace efficiency ratings are determined by testing the furnace’s performance in a laboratory setting. The rating is based on the amount of heat produced by the furnace compared to the amount of fuel consumed. Higher efficiency ratings indicate that the furnace is able to convert more fuel into heat, resulting in lower energy costs.
There are different types of gas furnace efficiency ratings to be aware of:
| AFUE | The Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating measures how efficiently the furnace converts fuel into heat over the course of a year. This rating considers the energy lost through venting and other factors. |
| ENERGY STAR | The ENERGY STAR rating is given to gas furnaces that meet or exceed specific efficiency criteria set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). These furnaces are designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. |
| SEER | The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating measures the efficiency of the air conditioning aspect of a gas furnace. This rating is important if your furnace has a built-in air conditioning unit. |
When choosing a gas furnace, it is important to consider the efficiency rating that best suits your needs. Higher efficiency ratings may come with a higher price tag, but they can result in significant energy savings over time. Consulting with a heating professional can help you determine the right efficiency rating for your home.
Types of Gas Furnace Efficiency Ratings
When it comes to gas furnace efficiency, there are different ratings that can help you understand how efficient a particular furnace is. These ratings are designed to provide consumers with information about the furnace’s energy consumption and performance. Here are some of the most common types of gas furnace efficiency ratings:
- AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) – This is the most widely recognized rating and measures the overall efficiency of a gas furnace over an entire heating season. The AFUE rating is expressed as a percentage and indicates how much of the fuel consumed by the furnace is converted into heat. The higher the AFUE rating, the more efficient the furnace.
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) – While SEER is typically used to measure the cooling efficiency of air conditioners and heat pumps, it can also be used to gauge the energy efficiency of gas furnaces with air conditioning capabilities. The SEER rating is calculated by dividing the cooling output of the unit by the amount of electricity consumed during a specific season.
- HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) – Much like the SEER rating, the HSPF rating is generally used to evaluate the efficiency of heat pumps. However, it can also be used to assess the heating efficiency of gas furnaces with heat pump capabilities. The HSPF rating is calculated by dividing the heating output of the system by the amount of electricity consumed during a specific season.
- ENERGY STAR® Certification – The ENERGY STAR certification is not a specific rating, but rather a distinction given to gas furnaces that meet or exceed certain energy efficiency criteria set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Gas furnaces with the ENERGY STAR label are typically more efficient and consume less energy compared to conventional models.
Understanding these different gas furnace efficiency ratings can help you make an informed decision when selecting a new furnace. It’s important to note that the highest efficiency rating may not always be the best choice for your specific needs, as factors such as climate and usage patterns can also impact the efficiency and performance of a gas furnace.
AFUE: Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency
AFUE, or Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency, is an important rating for understanding the efficiency of a gas furnace. It measures how efficiently a furnace converts fuel into usable heat over the course of a year.
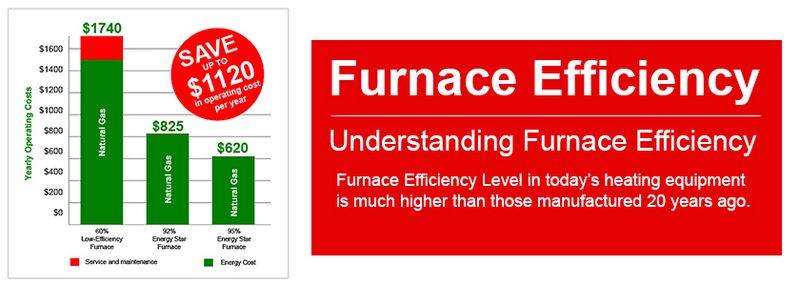
The AFUE rating is expressed as a percentage, and the higher the percentage, the more efficient the furnace. For example, a furnace with an AFUE rating of 95% means that 95% of the fuel it consumes is converted into heat, while the remaining 5% is lost through combustion gases.
AFUE ratings can vary depending on the type of furnace and the fuel it uses. Gas furnaces typically have AFUE ratings ranging from 80% to 98%. Higher AFUE ratings not only indicate a more efficient furnace, but also mean that less fuel is wasted and more heat is produced for the same amount of fuel consumed.
Understanding the AFUE rating of a furnace is important when considering energy efficiency and operating costs. A higher AFUE rating may result in lower fuel bills and reduced environmental impact. It can also help homeowners make informed decisions when choosing a furnace that meets their needs and budget.
It’s important to note that AFUE ratings are not the only factor to consider when evaluating furnace efficiency. Other factors, such as the furnace’s design, insulation, and maintenance, can also affect how efficiently it operates. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can provide further insight into choosing a furnace with the right AFUE rating for your home.
SEER: Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio
The SEER rating, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measure of the efficiency of an air conditioning system. While the AFUE rating is used to measure the efficiency of a gas furnace, the SEER rating is used to measure the efficiency of air conditioners and heat pumps.
The SEER rating is a ratio that represents the cooling output of an air conditioning system in British thermal units (BTUs) divided by the electrical energy input in watt-hours. This means that a higher SEER rating indicates a more energy-efficient system.
Understanding SEER ratings can help homeowners choose the most efficient air conditioning system for their needs. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-saving potential the system has. However, it’s important to note that a higher SEER rating often comes with a higher price tag.
To provide perspective, the government has set minimum SEER requirements for new air conditioning systems. As of January 1, 2015, the minimum SEER rating for new air conditioners and heat pumps is 14. This ensures that homeowners have access to energy-efficient options while also encouraging manufacturers to develop more efficient technologies.
In addition to the SEER rating, homeowners should also consider other factors such as the size of their space, climate, and usage patterns when choosing an air conditioning system. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can help homeowners make an informed decision and select the right system for their specific needs.
HSPF: Heating Seasonal Performance Factor
In understanding gas furnace efficiency, it is important to know about different ratings and what they mean. One such rating is the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF). HSPF is a measurement of the efficiency of a heat pump during the heating season.
HSPF is calculated by dividing the total heat output of a heat pump during its normal usage period by the total energy input during that same period. It takes into account the energy consumed by the heat pump as well as any auxiliary electric heat used.
A higher HSPF rating indicates a more efficient heat pump. In general, heat pumps with HSPF ratings of 8 or above are considered highly efficient. HSPF ratings can range from 6 to 10 or higher, depending on the specific model.
When comparing gas furnaces, it is important to consider both the AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) and the HSPF ratings. While the AFUE rating measures the efficiency of the gas furnace during the heating season, the HSPF rating specifically measures the efficiency of a heat pump.
By understanding the different ratings and what they mean, homeowners can make informed decisions about their gas furnace options. Choosing a gas furnace with high efficiency ratings such as a high AFUE and HSPF can help save energy and reduce heating costs in the long run.
EER: Energy Efficiency Ratio
The Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) is an important rating that helps consumers understand the efficiency of their gas furnace. The EER measures the cooling output of a furnace in relation to the amount of energy it consumes. It is calculated by dividing the cooling capacity (in British Thermal Units or BTUs) by the power input (in watts).
The EER rating is used primarily for air conditioning units, but it can also be applied to gas furnaces. A higher EER rating indicates a more efficient furnace, as it is able to produce more cooling output for the same amount of energy input. This means that a furnace with a higher EER rating will provide greater energy savings and lower operating costs.
It’s important to note that the EER rating is different from the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating, which is commonly used for gas furnaces. While the AFUE measures the efficiency of a furnace in converting fuel to heat, the EER focuses specifically on cooling efficiency. Therefore, it is crucial to consider both ratings when evaluating the overall efficiency of a gas furnace.
Understanding the EER rating of a gas furnace can help consumers make informed decisions when purchasing a new furnace. By choosing a furnace with a higher EER rating, homeowners can ensure they are getting a more efficient and cost-effective heating and cooling system.
COP: Coefficient of Performance
The coefficient of performance (COP) is an important measurement when it comes to understanding the efficiency of a gas furnace. It is a ratio that compares the amount of useful energy output of a heating system to the amount of energy input.
In the case of a gas furnace, the COP is calculated by dividing the heat output by the energy input. A higher COP indicates a more efficient furnace, as it means that more heat is being produced for a given amount of energy input.
The COP can be influenced by various factors, including the design and size of the furnace, the quality of the insulation, and the temperature conditions. It is important to consider the COP when selecting a gas furnace, as a higher COP can result in lower energy costs and increased comfort.
However, it is important to note that the COP is just one of the many ratings used to evaluate the efficiency of a gas furnace. Other important ratings include the annual fuel utilization efficiency (AFUE) and the heating seasonal performance factor (HSPF).
By understanding the different ratings and what they mean, homeowners can make more informed decisions when it comes to selecting a gas furnace that best meets their needs and budgets. It is always recommended to consult with a qualified HVAC professional to determine the most suitable furnace for your specific requirements.
Understanding AFUE: What Does It Mean?
When it comes to understanding the efficiency of a gas furnace, one of the most important ratings to consider is the AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency). But what exactly does AFUE mean?
AFUE is a measure of how efficiently a gas furnace converts fuel into usable heat over the course of a year. It is expressed as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating a more efficient furnace. For example, an AFUE rating of 95% means that 95% of the fuel consumed by the furnace is converted into heat, while the remaining 5% is lost through the exhaust.
To put it simply, AFUE is a way to evaluate the energy efficiency of a gas furnace. A furnace with a higher AFUE rating will have lower operating costs and consume less fuel, making it more environmentally friendly and cost-effective in the long run.
It’s important to note that AFUE is a standard that is regulated and certified by industry organizations, ensuring that consumers can trust the ratings provided by manufacturers. This allows homeowners to easily compare the efficiency of different gas furnaces and make informed decisions when purchasing a new one.
When comparing AFUE ratings, it’s also important to consider the climate in which the furnace will be used. A higher AFUE rating may be more beneficial in colder climates, where the furnace will be used for a longer duration, while a lower AFUE rating may be sufficient in milder climates.
In conclusion, understanding the AFUE rating is essential when evaluating the efficiency of a gas furnace. By considering this rating along with other factors such as climate and energy prices, homeowners can make informed decisions and choose the most efficient furnace for their needs.
How to Calculate AFUE
AFUE, or Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency, is a measurement that indicates the efficiency of a gas furnace. It measures the amount of heat produced by a furnace compared to the amount of fuel consumed, expressed as a percentage. The higher the AFUE rating, the more efficient the furnace.
To calculate AFUE, you need to know the amount of heat produced by the furnace and the amount of fuel consumed. The formula for calculating AFUE is:
AFUE = (Heat Produced / Fuel Consumed) x 100
The heat produced by the furnace is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs), while the fuel consumed is measured in gallons of fuel or cubic feet of natural gas. By dividing the heat produced by the fuel consumed, you can determine the efficiency of the furnace.
For example, if a furnace produces 100,000 BTUs of heat and consumes 90 gallons of fuel, the AFUE can be calculated as follows:
AFUE = (100,000 BTUs / 90 gallons) x 100 = 111.11%
In this example, the AFUE of the furnace is 111.11%. This means that the furnace is able to convert 111.11% of the fuel it consumes into usable heat.
It is important to note that AFUE is an average measurement and may not accurately represent the actual energy efficiency of a furnace in all operating conditions. Factors such as temperature variations, ductwork design, and home insulation can impact the overall efficiency of a furnace.
When comparing different gas furnaces, it is important to consider the AFUE rating to determine their efficiency and potential energy savings. Higher AFUE ratings generally indicate more efficient furnaces, which can result in lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact.
Comparing AFUE Ratings: What to Look For
When it comes to understanding furnace efficiency, it’s important to be familiar with the different ratings that are used to measure it. One of the most important ratings to consider is the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating.
The AFUE rating is a percentage that shows how much of the fuel used by a gas furnace is converted into usable heat. For example, if a furnace has an AFUE rating of 95%, it means that 95% of the fuel is converted into heat, while the remaining 5% is lost as waste. A higher AFUE rating indicates a more efficient furnace.
When comparing AFUE ratings, it’s important to look for several key factors:
| 1. Energy Savings | A furnace with a higher AFUE rating will provide greater energy savings compared to a furnace with a lower rating. This can result in lower utility bills and a more environmentally-friendly heating system. |
| 2. Operating Costs | A furnace with a higher AFUE rating will typically have lower operating costs since it is more efficient at converting fuel into heat. This can lead to long-term savings over the lifespan of the furnace. |
| 3. System Performance | A furnace with a higher AFUE rating will generally provide better heating performance and more consistent comfort throughout the home. This is because the furnace is able to convert a larger percentage of the fuel into usable heat. |
| 4. Rebates and Incentives | Many utility companies and government programs offer rebates and incentives for homeowners who purchase high-efficiency furnaces with a certain AFUE rating. Checking for these opportunities can help offset the initial cost of the furnace. |
Overall, comparing AFUE ratings is essential in making an informed decision when choosing a gas furnace. By understanding what the ratings mean and considering factors such as energy savings, operating costs, system performance, and potential rebates, homeowners can ensure they are selecting a furnace that meets their heating needs efficiently.
SEER vs. AFUE: Which is More Important?
SEER is a rating used to measure the efficiency of air conditioning systems, including the cooling process. It represents the ratio of the cooling output to the amount of energy consumed during a typical cooling season. A higher SEER rating indicates a more energy-efficient system, resulting in lower electricity bills and reduced environmental impact.
On the other hand, AFUE focuses on the efficiency of the heating aspect of a gas furnace. It measures the amount of heat produced by the furnace compared to the amount of fuel consumed. Essentially, AFUE tells you how well the furnace converts fuel into usable heat. A higher AFUE rating means that more energy is being utilized for heating, resulting in lower heating costs.
Both SEER and AFUE ratings are crucial in determining the overall efficiency of a gas furnace, but their importance depends on your specific needs. If you live in a region with a long and hot summer, and use your air conditioner frequently, a high SEER rating can result in significant energy savings. On the other hand, if you rely heavily on heating your home during the winter, a high AFUE rating will help you save on heating costs.
Understanding the differences between SEER and AFUE is essential when choosing a gas furnace. While both ratings contribute to overall efficiency, their focus on cooling and heating efficiency makes them suitable for different purposes. Consider your climate, usage patterns, and energy priorities to determine which rating is more important for your specific needs.
HSPF vs. AFUE: Comparing Heating Efficiency Ratings
When it comes to understanding the efficiency ratings of a gas furnace, it’s important to know the difference between HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) and AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency). These two ratings provide valuable information about how efficiently a furnace can convert fuel into heat.
HSPF specifically measures the efficiency of a heat pump in heating mode. It takes into account the total heating output produced by a heat pump during a typical heating season, divided by the total amount of electricity consumed during that same period. The higher the HSPF rating, the more efficient the heat pump is at heating your home.
On the other hand, AFUE measures the efficiency of a furnace in converting fuel into usable heat over the course of an entire year. It represents the percentage of fuel that is actually turned into heat, with the rest being lost through combustion or other means. AFUE ratings are commonly used for gas and oil furnaces. The higher the AFUE rating, the more efficient the furnace is at converting fuel into heat.
While both HSPF and AFUE provide information about the efficiency of a heating system, it’s important to understand that they measure different aspects of efficiency. HSPF focuses on the efficiency of a heat pump’s heating mode, while AFUE measures the overall efficiency of a furnace throughout an entire year.
When comparing heating efficiency ratings, it’s important to consider your specific heating needs and climate. HSPF may be a more relevant rating to consider if you primarily rely on a heat pump for heating. However, if you have a gas or oil furnace, AFUE will be the rating that provides a better understanding of its efficiency.
In summary, HSPF and AFUE are both important efficiency ratings for heating systems. Understanding the differences between these two ratings can help you make informed decisions when it comes to choosing the most efficient furnace for your home.
EER vs. AFUE: Comparing Cooling and Heating Efficiency
When it comes to gas furnaces, understanding the different ratings is essential to determine their efficiency. Two important ratings to consider for both cooling and heating efficiency are the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE).
The EER is a measure of the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner or heat pump. It is calculated by dividing the cooling output (in British thermal units or BTUs) by the electrical input (in watts) during a typical cooling season. The higher the EER rating, the more efficient the cooling system is. This is important for homeowners who live in warm climates and rely on their air conditioners or heat pumps for cooling their homes.
The AFUE, on the other hand, is a measure of the heating efficiency of a gas furnace. It is calculated by dividing the heat output (in BTUs) by the fuel input (in BTUs) during a typical heating season. The AFUE rating represents the percentage of fuel that is actually converted into usable heat. For example, a furnace with a 90% AFUE rating converts 90% of the fuel into heat, while the remaining 10% is lost through combustion gases or other means. The higher the AFUE rating, the more efficient the furnace is at converting fuel into heat.
Comparing the EER and AFUE ratings can help homeowners understand the overall efficiency of their cooling and heating systems. While the EER focuses on cooling efficiency and is usually used for air conditioners and heat pumps, the AFUE focuses on heating efficiency and is used for gas furnaces. It is important to note that these ratings are not directly comparable, as they measure different aspects of efficiency.
When choosing a gas furnace, homeowners should consider both the EER and AFUE ratings to ensure optimal energy efficiency and cost savings. It is recommended to look for furnaces with higher AFUE ratings, as they will provide greater efficiency and potentially lower heating costs in the long run. Additionally, selecting a furnace with a high EER rating can contribute to lower cooling costs, especially in warmer climates.
In conclusion, understanding the EER and AFUE ratings is crucial when evaluating the efficiency of cooling and heating systems. By comparing these ratings, homeowners can make informed decisions and choose the most efficient and cost-effective options for their homes.
COP vs. AFUE: A Look at Heat Pump Efficiency
Heat pump efficiency is typically measured using two different ratings: the coefficient of performance (COP) and the annual fuel utilization efficiency (AFUE). While both ratings provide information about the efficiency of a heat pump system, they do so in different ways.
The COP is a measurement of the heat produced by the heat pump compared to the electrical energy consumed. It is calculated by dividing the heat output by the electrical input. A higher COP indicates a more efficient system, as it is able to produce more heat with less electricity.
The AFUE, on the other hand, is a measurement of the heat produced by the heat pump compared to the total energy consumed, including both electrical energy and any additional fuel used. It is calculated by dividing the heat output by the total energy input. A higher AFUE indicates a more efficient system, as it is able to produce more heat with less overall energy consumption.
Both the COP and AFUE ratings are important for understanding the efficiency of a heat pump system. However, it is important to note that the COP is typically used to measure the efficiency of the heating mode, while the AFUE is used to measure the efficiency of the entire system over an entire heating season.
In summary, the COP and AFUE ratings provide different perspectives on heat pump efficiency. While the COP focuses on the heat produced compared to the electrical energy consumed, the AFUE takes into account the total energy consumption of the system. Understanding both ratings can help homeowners make informed decisions about the most efficient heat pump system for their needs.
Which Efficiency Ratings Should You Prioritize?
When it comes to understanding the efficiency of a gas furnace, there are different ratings to consider. These ratings provide valuable information about how well a furnace performs and the energy it consumes. Here is a breakdown of the different efficiency ratings and what they mean:
- AFUE Rating: The Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating is one of the most important ratings to prioritize when choosing a gas furnace. It measures the efficiency of a furnace over the course of a heating season. The higher the AFUE rating, the more efficiently the furnace converts fuel into heat.
- ENERGY STAR® Certification: If a gas furnace has the ENERGY STAR® certification, it means that it meets the strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Look for a furnace with this certification to ensure high energy efficiency and potential savings on utility bills.
- SEER Rating: While not specific to gas furnaces, the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating measures the cooling efficiency of air conditioning systems. It is worth considering if you are also looking for a furnace with built-in air conditioning capabilities.
- HSPF Rating: Similar to the SEER rating, the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) measures the efficiency of heat pumps in both heating and cooling modes. If you are considering a heat pump for your heating needs, keep this rating in mind.
- MCAA Efficiency Rating: The Mechanical Contractors Association of America (MCAA) has its own efficiency rating system for gas furnaces. This rating accounts for various factors, such as the design of the heat exchanger, burner, and controls. A furnace with a higher MCAA Efficiency Rating indicates better overall performance.
When choosing a gas furnace, it is important to consider all of these ratings to ensure you are getting the most efficient unit for your needs. Prioritizing the AFUE rating and ENERGY STAR® certification is a good starting point, but it ultimately depends on your specific requirements and the climate in which you live.
Q&A:
What is the importance of gas furnace efficiency ratings?
Gas furnace efficiency ratings are important because they help homeowners understand how effective a furnace is at converting fuel into heat. The higher the rating, the more efficient the furnace is, which means lower energy bills and less environmental impact.
What do AFUE and HSPF stand for?
AFUE stands for Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency, and HSPF stands for Heating Seasonal Performance Factor. These are two common ratings used to measure the efficiency of gas furnaces. AFUE measures the efficiency of furnaces over the course of a year, while HSPF measures the efficiency of heat pumps.
How do AFUE and HSPF ratings affect energy consumption?
AFUE and HSPF ratings directly affect energy consumption. The higher the AFUE rating, the less energy a furnace consumes to produce heat. Similarly, a higher HSPF rating means a heat pump is more efficient at converting electricity into heat. So, higher ratings result in lower energy bills.
What is the minimum AFUE rating for gas furnaces?
The minimum AFUE rating for gas furnaces in the United States is currently 80%. This means that a furnace must be able to convert at least 80% of the fuel it consumes into heat. However, there are more efficient options available with AFUE ratings of 90% or higher.
What factors affect the efficiency of a gas furnace?
There are several factors that affect the efficiency of a gas furnace. These include the type and quality of the furnace, the size and insulation of the home, the climate, and how well the furnace is maintained. It is important to consider all of these factors when choosing a furnace for optimal efficiency.






