Demystifying SEER Ratings: Its Significance in HVAC Efficiency
Ratings play a crucial role in determining the efficiency of HVAC systems, and the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating is one of the most important factors to consider. In the world of HVAC, understanding the significance of SEER ratings is essential for homeowners and industry professionals alike.
The SEER rating measures the efficiency of an HVAC system by calculating the cooling output compared to the energy input over a typical cooling season. A higher SEER rating indicates a more efficient system, which translates to lower energy consumption and reduced utility costs. This is especially significant considering that HVAC systems are responsible for a significant portion of a home’s energy usage.
When it comes to HVAC efficiency, the SEER rating is the gold standard. It helps consumers make informed decisions when selecting an HVAC system by comparing different models and brands. The higher the SEER rating, the greater the energy savings and environmental benefits. This rating also serves as a benchmark for manufacturers to continuously improve their technology and produce more energy-efficient HVAC systems.
In summary, understanding SEER ratings is crucial for optimizing HVAC efficiency. Homeowners looking to reduce their energy consumption and utility bills should prioritize selecting a system with a higher SEER rating. Likewise, industry professionals can use SEER ratings to educate customers on the benefits of energy-efficient HVAC systems and help guide them towards smart investments. With the increasing focus on sustainability and energy conservation, SEER ratings play a vital role in shaping the future of HVAC technology.
What Are SEER Ratings?
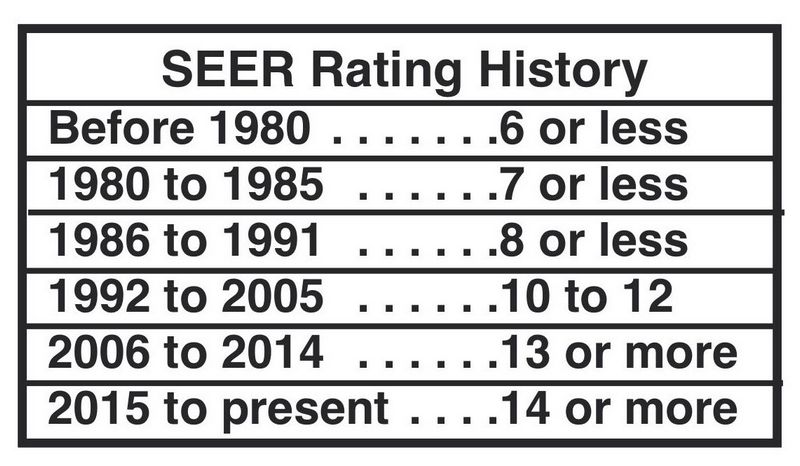
SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, and it is a ratings system that helps demystify the efficiency of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. The SEER rating indicates the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner or heat pump. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the HVAC system is.
SEER ratings are significant because they measure the amount of cooling output an air conditioner or heat pump provides for each unit of energy it consumes. This means that a higher SEER rating signifies a system that can deliver more cooling power while using less energy, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
Understanding SEER ratings is essential when shopping for a new HVAC system. The minimum SEER rating standard set by the U.S. Department of Energy is 13. However, more energy-efficient systems can have SEER ratings of 14 or higher. Investing in a higher SEER-rated system may incur a higher upfront cost, but it can result in significant long-term savings and environmental benefits.
It is important to note that SEER ratings only apply to the cooling performance of an HVAC system and do not factor in heating efficiency. For a complete understanding of an HVAC system’s overall efficiency, it is recommended to consider the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) for heat pumps.
In summary, SEER ratings are a vital tool in assessing the energy efficiency of HVAC systems. They help consumers make informed decisions when purchasing new equipment and can contribute to reducing energy consumption and utility costs.
How Do SEER Ratings Affect HVAC Efficiency?
The demystifying world of HVAC efficiency is closely associated with SEER ratings. SEER, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measure of how efficient an air conditioning unit or heat pump is at cooling your home. Essentially, the higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the system is in converting energy into cooled air.
The SEER rating takes into account the cooling output of an HVAC system over a cooling season, divided by the total electrical energy input during that same period. This ratio allows homeowners to compare different models and make an informed decision when purchasing a new HVAC system.
Higher SEER ratings indicate a higher level of energy efficiency. HVAC systems with higher SEER ratings are designed to consume less electricity while providing the same amount of cooling as systems with lower ratings. Consequently, these efficient systems can help homeowners save money on their energy bills in the long run.
It’s important to note that SEER ratings are not static and can vary depending on various factors, such as the size of the unit, the location where it is installed, and climate conditions. A professional HVAC contractor can help determine the appropriate SEER rating for your specific needs and location.
In summary, SEER ratings play a crucial role in determining the efficiency of an HVAC system. By understanding the SEER rating and its impact on energy consumption, homeowners can make informed decisions when selecting an HVAC unit, ultimately leading to lower energy bills and a more comfortable living environment.
The Importance of Understanding SEER Ratings for Your HVAC System
When it comes to evaluating the efficiency of HVAC systems, one term that is of significant importance is SEER ratings. SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, and it is a rating that measures how efficiently an air conditioning unit or heat pump can cool or heat a space.
SEER ratings play a crucial role in determining the energy efficiency of HVAC systems. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy efficient the unit is, which translates to lower energy consumption and, ultimately, lower utility bills.
Understanding SEER ratings is essential for homeowners and business owners looking to make informed decisions when it comes to purchasing or upgrading their HVAC systems. By demystifying SEER ratings, customers can better assess the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of different models and choose the one that best suits their needs and budget.
By considering SEER ratings, you can not only contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future but also save money in the long run. HVAC systems with higher SEER ratings are not only more energy efficient but also tend to have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
When shopping for a new HVAC system, it is crucial to pay attention to SEER ratings and consider the long-term benefits of investing in a more efficient unit. By understanding SEER ratings, you can make an informed decision and choose an HVAC system that not only provides optimal comfort but also maximizes energy savings and minimizes environmental impact.
What Is the Meaning of SEER Ratings?
When it comes to HVAC systems, SEER ratings carry significant importance in determining their efficiency. SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio and is used to demystify the efficiency levels of cooling equipment.
The SEER rating represents the cooling output of an air conditioner or heat pump during a typical cooling season, divided by the energy it consumes in Watt-hours. In simpler terms, the higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the HVAC system is in converting electricity into cooling power.
SEER ratings provide consumers with a standardized way to compare the efficiency of different models. By selecting a higher SEER-rated system, homeowners can enjoy increased energy savings and lower utility bills.
It’s important to note that SEER ratings only represent the efficiency of cooling equipment and do not take heating efficiency into account. For a comprehensive evaluation of system efficiency, homeowners should consider other ratings such as HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) for heat pumps and AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) for furnaces.
When purchasing an HVAC system, it is recommended to choose a SEER rating that matches the climate conditions of your area. Warmer climates typically benefit from higher SEER ratings, as the system needs to work harder to cool the indoor space. However, it’s essential to find a balance between efficiency and cost, as higher SEER-rated systems tend to have a higher upfront cost.
In conclusion, SEER ratings provide consumers with a straightforward way to understand and compare the efficiency of HVAC systems. By considering the SEER rating alongside other relevant ratings, homeowners can make informed decisions about their heating and cooling needs, ultimately saving energy and money in the long run.
How Are SEER Ratings Calculated?
The significance of SEER ratings in the HVAC industry cannot be overstated. SEER, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioning system over a typical cooling season. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the system is.
SEER ratings are calculated by looking at the cooling output of an air conditioning system divided by the electrical energy input. This calculation is done over a specific period, usually a cooling season, to provide an accurate representation of the system’s efficiency.
To better understand how SEER ratings are calculated, let’s take a look at the formula:
| = | Cooling Output (BTUs) | ÷ | Electrical Energy Input (Watts) |
The cooling output is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs), which is a unit of heat. The electrical energy input is measured in Watts, which is a unit of power. By dividing the cooling output by the electrical energy input, we get the SEER rating.
SEER ratings play a crucial role in demystifying HVAC efficiency. They provide a standardized measure of how efficiently an air conditioning system can cool a space. Homeowners and HVAC professionals can use SEER ratings to compare different systems and make informed decisions when it comes to purchasing or replacing their air conditioning units.
In summary, SEER ratings are calculated by dividing the cooling output of an air conditioning system by the electrical energy input over a specific period. This calculation provides a measure of the system’s efficiency and helps homeowners and professionals understand the performance of different HVAC systems.
SEER Ratings vs. EER Ratings: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the efficiency of HVAC systems can be a bit daunting with all the different ratings and acronyms. Among the most commonly mentioned ratings are SEER and EER. While both ratings are indicators of the efficiency of an HVAC system, there are some key differences between them.
SEER, which stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a rating that measures the cooling efficiency of an HVAC system over an entire cooling season. It takes into account factors such as temperature fluctuations and varying usage patterns. SEER ratings are typically higher than EER ratings, as they provide a more comprehensive measurement of efficiency under real-world conditions.
EER, on the other hand, stands for Energy Efficiency Ratio. It is a rating that measures the cooling efficiency of an HVAC system under specific conditions, namely a constant indoor and outdoor temperature. EER provides a more static measurement of efficiency, which can be useful for comparing different models or sizing systems for specific applications.
It’s important to note that both SEER and EER ratings are calculated using standardized testing procedures set by the Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI). These ratings help consumers make informed decisions about the efficiency of their HVAC systems and the potential energy savings they can achieve.
In summary, SEER ratings provide a more comprehensive measure of efficiency over an entire cooling season, accounting for real-world conditions and usage patterns. EER ratings, on the other hand, offer a more static measurement of efficiency under specific conditions. Both ratings are valuable in their own right and can help consumers choose the most efficient HVAC system for their needs.
Demystifying these HVAC ratings is essential for understanding the true efficiency of different systems and making informed decisions about energy consumption and potential savings. So, whether you’re shopping for a new HVAC system or looking to optimize the efficiency of your existing one, understanding the difference between SEER and EER ratings is key.
How Do SEER Ratings Impact Energy Consumption?
SEER ratings play a crucial role in determining the energy efficiency of HVAC systems. Understanding these ratings is key to demystifying the efficiency levels of your HVAC system.
SEER, which stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, measures the cooling output of an HVAC system over a typical cooling season, divided by the energy it consumes in Watt-Hours. In simple terms, it tells you how efficiently your system uses electricity to cool your home.
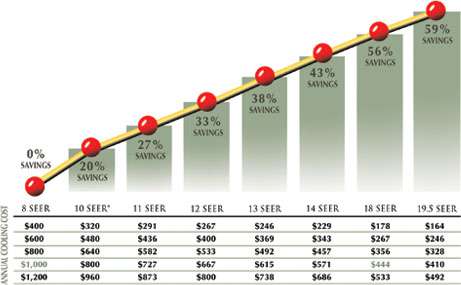
The higher the SEER rating of your HVAC system, the more energy-efficient it is. This means that a system with a higher SEER rating will consume less energy to provide the same cooling output compared to a system with a lower SEER rating. This can result in significant energy savings and lower utility bills over time.
For example, consider the following:
Let’s say you have an older HVAC system with a SEER rating of 10. If you replace it with a new system with a SEER rating of 16, you can expect to reduce your energy consumption by up to 60%. This means that you will save 60% on your cooling energy costs compared to your older system.
It’s important to note that SEER ratings are determined under specific conditions. Real-world performance may vary depending on factors such as climate, indoor and outdoor temperature, humidity levels, and the quality of the installation.
In addition to energy savings, systems with higher SEER ratings also tend to offer better comfort and quieter operation. They are designed to provide more precise temperature control and maintain a consistent indoor temperature.
To summarize, understanding SEER ratings is essential for homeowners and HVAC professionals alike. Higher SEER ratings can lead to significant energy savings and improved comfort levels, making them a crucial factor to consider when upgrading or installing a new HVAC system.
The Benefits of Choosing a High SEER Rated HVAC System
When it comes to selecting an HVAC system for your home or office, understanding the efficiency ratings can be demystifying. One key rating to consider is the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating. This rating measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioning unit or heat pump, and choosing a system with a high SEER rating can offer numerous benefits.
The significance of a high SEER rating lies in its ability to provide improved energy efficiency. HVAC systems with higher SEER ratings consume less energy to deliver the same cooling or heating output as systems with lower ratings. This means that you can enjoy a comfortable indoor environment while saving on energy costs.
Another benefit of choosing a high SEER rated HVAC system is its environmental impact. By reducing energy consumption, these systems help to lower greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. By investing in a high SEER rated system, you can do your part in protecting the environment.
Furthermore, HVAC systems with high SEER ratings often come with advanced features and technologies that enhance comfort and convenience. These systems may include variable-speed compressors, smart thermostats, and zoning capabilities, allowing you to customize your indoor climate according to your preferences and maximize comfort.
Choosing a high SEER rated HVAC system can also positively impact the value of your property. As energy efficiency becomes increasingly important to homeowners and businesses, having a high SEER rated system can be seen as an attractive feature. Potential buyers or tenants may be willing to pay a higher price or rent for a property that already has an energy-efficient HVAC system in place.
In conclusion, the benefits of choosing a high SEER rated HVAC system are clear. By improving energy efficiency, reducing environmental impact, enhancing comfort, and adding value to your property, these systems are an excellent investment for both your pocket and the planet.
Factors That Can Affect SEER Ratings
When it comes to understanding the efficiency of HVAC systems, the SEER ratings play a significant role. However, there are various factors that can affect these ratings, and it’s essential to demystify them to ensure a clear understanding of the significance they hold. Below are some key factors that can impact SEER ratings:
- Size of the HVAC System: The size of the HVAC system can greatly influence the SEER ratings. An oversized system may have a lower SEER rating as it won’t operate efficiently at partial loads, while an undersized system may also have a lower SEER rating due to increased strain on the components.
- Installation Quality: Proper installation is crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency. Factors such as ductwork design, insulation, and sealing can impact the SEER ratings. Any improperly installed components can lead to energy losses and reduced efficiency.
- Maintenance and Regular Servicing: Regular maintenance and servicing are essential for maintaining the efficiency of an HVAC system. Neglecting routine cleaning, filter replacements, and system inspections can lead to decreased airflow, higher energy consumption, and lower SEER ratings.
- Climate and Region: The climate and region where the HVAC system is installed can also affect SEER ratings. A higher SEER rating may be required in hotter climates to ensure the system can efficiently cool the space. On the other hand, in colder regions, the emphasis may be more on heating efficiency, leading to lower SEER ratings.
- Insulation and Building Envelope: The insulation and overall building envelope play a role in the SEER ratings. A well-insulated building with proper sealing can minimize energy losses and allow the HVAC system to operate more efficiently, resulting in higher SEER ratings.
- User Behavior and Settings: User behavior and settings also impact SEER ratings. Factors such as thermostat settings, temperature preferences, and usage habits can influence the energy consumption and efficiency of the system. Proper user education and energy-saving practices can contribute to higher SEER ratings.
By considering these factors that can affect SEER ratings, you can make informed decisions when choosing and maintaining an HVAC system. Understanding the significance of SEER ratings and how they can be influenced will help you optimize energy efficiency and ensure optimal comfort in your space.
SEER Ratings and Environmental Impact
The SEER rating is a key measure of efficiency for HVAC systems, and it also has an impact on the environment. By demystifying SEER ratings and understanding how they relate to energy efficiency, we can make more informed choices that reduce our carbon footprint and contribute to a sustainable future.
SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, and it measures the cooling output of an air conditioner or heat pump divided by the amount of electrical energy it consumes over a typical cooling season. In simple terms, the higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the HVAC system is at cooling.
Higher SEER ratings mean more energy savings, which in turn translates to reduced greenhouse gas emissions. By choosing a system with a higher SEER rating, you can reduce the amount of electricity needed to keep your home comfortable, helping to protect the environment and combat climate change.
When shopping for a new HVAC system, look for models with the highest SEER ratings that fit within your budget. Energy-efficient systems may have a higher upfront cost, but the long-term energy savings can often outweigh the initial investment.
Furthermore, selecting an HVAC system with a high SEER rating can make a significant difference in your energy bills. By reducing your overall energy consumption, you not only save money but also reduce demand on natural resources and decrease pollution.
In conclusion, understanding SEER ratings and their environmental impact is crucial for making informed choices when it comes to HVAC systems. By prioritizing energy efficiency and choosing systems with higher SEER ratings, we can contribute to a more sustainable future and help protect the planet for future generations.
Choosing the Right SEER Rating for Your Climate
When it comes to HVAC systems, understanding the significance of SEER ratings is essential. SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings demystify the efficiency of your cooling system. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient your HVAC system will be, resulting in lower energy consumption and decreased utility bills.
However, it’s important to choose the right SEER rating for your specific climate. Factors like temperature and humidity levels can greatly impact the performance of your HVAC system. Here are some tips to help you choose the right SEER rating:
1. Evaluate your climate: Take into consideration the average summer temperatures and humidity levels in your area. If you live in a region with hot, humid summers, you may want to consider a higher SEER rating to ensure optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
2. Calculate potential savings: Determine how much you can potentially save on energy costs by choosing a higher SEER rating. While systems with higher ratings may have a higher upfront cost, they can often provide significant long-term savings.
3. Consider your usage: Assess how often you use your cooling system and for how long. If you rely heavily on air conditioning throughout the year, investing in a higher SEER rating may be more beneficial in the long run.
4. Consult a professional: It’s always a good idea to consult with a qualified HVAC professional who can assess your specific needs and recommend the most suitable SEER rating for your climate and budget.
By choosing the right SEER rating for your climate, you can ensure that your HVAC system operates efficiently and provides you with optimal comfort throughout the year. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice and make an informed decision based on your specific requirements.
Understanding SEER Ratings: FAQs
When it comes to HVAC efficiency, understanding SEER ratings is key. SEER, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measurement that demystifies the efficiency of HVAC systems. Below, we answer some frequently asked questions about SEER ratings and their significance:
- 1. What is a SEER rating?
- 2. How is the SEER rating determined?
- 3. Why are SEER ratings important?
- 4. What is the significance of a higher SEER rating?
- 5. What is the minimum SEER rating for new HVAC systems?
- 6. Can I improve the SEER rating of my existing HVAC system?
- 7. Should I always choose the HVAC system with the highest SEER rating?
A SEER rating is a measure of an HVAC system’s efficiency. It represents the ratio of cooling output divided by the electrical input over a typical cooling season.
The SEER rating is determined by conducting tests on the HVAC system in a controlled environment. These tests measure the system’s cooling output and electrical input to calculate its efficiency.
SEER ratings are important because they help consumers compare the efficiency of different HVAC systems. Higher SEER ratings indicate higher efficiency and potentially lower energy costs.
A higher SEER rating means that the HVAC system is more efficient. Systems with higher SEER ratings require less energy to produce the same cooling output, resulting in lower energy bills.
The minimum SEER rating for new HVAC systems varies by region. In the United States, the minimum SEER rating for air conditioners is currently 14, while heat pumps have a minimum SEER rating of 8.2.
It is not possible to directly improve the SEER rating of an existing HVAC system. However, regular maintenance and proper use can help optimize its efficiency and performance.
Choosing the HVAC system with the highest SEER rating may not always be the best option. Factors such as climate, usage patterns, and budget should also be considered when selecting a system.
By understanding SEER ratings and their significance, consumers can make informed decisions when it comes to selecting an HVAC system that offers both efficiency and cost savings.
Common Misconceptions About SEER Ratings
SEER ratings have great significance when it comes to understanding the efficiency of HVAC systems, but there are often misconceptions surrounding them. By demystifying these misconceptions, you can make more informed decisions when it comes to choosing an energy-efficient HVAC system.
One common misconception is that a higher SEER rating automatically translates to better efficiency. While a higher SEER rating does indicate better efficiency, it’s important to consider other factors as well. The size and design of your HVAC system, the quality of installation, and proper maintenance all play a role in overall efficiency.
Another misconception is that a higher SEER rating will always result in significant energy savings. While it’s true that a higher SEER rating can lead to energy savings, the actual amount will depend on various factors, such as the climate you live in, the size of your home, and your usage patterns. It’s important to consider these factors and evaluate the potential energy savings realistically.
Some people also believe that upgrading to a higher SEER-rated system will automatically save them money. While this can be true in certain circumstances, it’s not always the case. The upfront cost of a higher SEER-rated system is typically higher, and it may take several years of energy savings to recoup the initial investment. It’s essential to weigh the upfront cost against the potential long-term savings before making a decision.
It’s also worth mentioning that SEER ratings only measure cooling efficiency. They do not account for heating efficiency. If you are looking for optimal efficiency year-round, it’s important to consider both the SEER rating and the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) when choosing an HVAC system.
To sum up, understanding the significance of SEER ratings is crucial for evaluating the efficiency of HVAC systems. However, it’s essential to dispel common misconceptions and consider various factors, such as system size, installation quality, climate, and usage patterns, in order to make well-informed decisions about energy efficiency and potential cost savings.
Q&A:
What is a SEER rating?
A SEER rating, or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, is a measure of how efficiently an HVAC system operates over an entire cooling season. It represents the cooling output (in BTUs) divided by the electrical energy input (in watt-hours).
How is the SEER rating calculated?
The SEER rating is calculated by taking the total cooling output of an HVAC system over a cooling season and dividing it by the total electrical energy input. The resulting value is an indication of how efficiently the system operates.
What is a good SEER rating for an HVAC system?
A good SEER rating for an HVAC system is typically considered to be around 15 or higher. Higher SEER ratings indicate greater energy efficiency and can result in lower energy bills.
What are the benefits of a high SEER rating?
A high SEER rating for an HVAC system can provide several benefits. It can result in lower energy bills, as the system is more efficient and requires less electricity to operate. Additionally, a high SEER rating can contribute to a more comfortable indoor environment and may even increase the resale value of a home.
Are there any drawbacks to choosing a system with a high SEER rating?
While there are many benefits to choosing a system with a high SEER rating, there are also a few drawbacks to consider. Systems with higher SEER ratings tend to be more expensive upfront. Additionally, they may require more regular maintenance and specialized equipment for installation and repairs.
What is a SEER rating?
A SEER rating stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio and it measures the efficiency of an HVAC system. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy efficient the system is.






